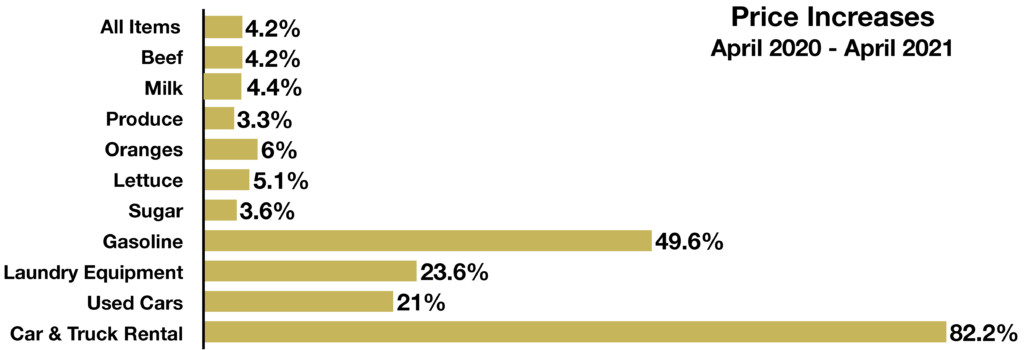Robert Krueger
Alexander Randolph Advisory Inc.
8200 Greensboro Drive, Suite 1125
McLean, VA 22102
703.734.1507
Stock Indices:
| Dow Jones | 47,716 |
| S&P 500 | 6,849 |
| Nasdaq | 23,365 |
Bond Sector Yields:
| 2 Yr Treasury | 3.47% |
| 10 Yr Treasury | 4.02% |
| 10 Yr Municipal | 2.74% |
| High Yield | 6.58% |
YTD Market Returns:
| Dow Jones | 12.16% |
| S&P 500 | 16.45% |
| Nasdaq | 21.00% |
| MSCI-EAFE | 24.26% |
| MSCI-Europe | 27.07% |
| MSCI-Emg Asia | 26.34% |
| MSCI-Emg Mkt | 27.10% |
| US Agg Bond | 7.46% |
| US Corp Bond | 7.99% |
| US Gov’t Bond | 7.17% |
Commodity Prices:
| Gold | 4,253 |
| Silver | 57.20 |
| Oil (WTI) | 59.53 |
Currencies:
| Dollar / Euro | 1.15 |
| Dollar / Pound | 1.32 |
| Yen / Dollar | 156.21 |
| Canadian /Dollar | 0.71 |
July 2021 |
Macro Overview
Financial global markets are drawing support from the effectiveness of ongoing vaccinations and improving economic indicators. Consumer sentiment is re-evolving, resulting in rising consumer demand as pandemic worries wane. Pent up demand from the past year is thought to be driving the bulk of economic activity.
Ransomeware cyberattacks and internet crimes have been rising at an alarming rate according to the FBI, threatening companies, government entities and individuals. Digital currencies, such as bitcoin, are the primary form of payment utilized for ransom and extortion cases since payments can be made anonymously and are not traceable. The FBI encourages individuals, especially elders, to be aware of numerous online scams and phone calls by visiting its Common Scams & Crimes site https://www.fbi.gov/scams-and-safety/common-scams-and-crimes.
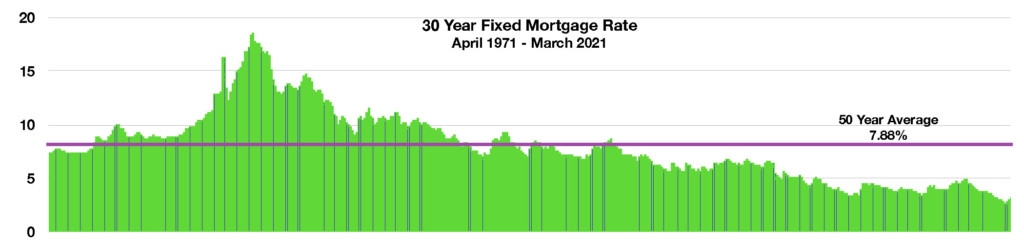
Escalating inflation concerns prompted Federal Reserve members to consider limiting purchases of Treasury and mortgage bonds, which is an indirect method of raising interest rates. The reduction in stimulus efforts, also known as tapering, last occurred in 2013.
The administration released a proposed $6 trillion federal budget for the upcoming fiscal year, expected to be funded by higher taxes for top earners and corporations. Analysts, as well as nonpartisan analysis, expect additional issuance of Treasury debt in order to help fund ongoing federal deficits.
Various states are ending supplemental unemployment benefits which were instituted during the early months of the pandemic last year. It is estimated that 3.7 million unemployed recipients will be affected. Some states eliminating unemployment benefits are instead offering financial incentives for individuals to find a job. The Department of Labor’s most recent data reveal that there were over 8 million unfilled job openings at the end of March, the largest number of openings since November 2018.
An increase in travel has spurred higher fuel costs for airlines and automobiles as pent up demand and the summer months propel prices higher. The average cost for a gallon of regular gasoline rose above $3 per gallon nationally in May, the highest since 2014. Crude oil prices, which directly affect the price of gasoline, have risen over 80% in the past year.
Sources: FBI, Federal Reserve, EIA, Dept. of Labor