
Earl R. King Sr., CFP®
Managing Member
9701 Apollo Drive, Suite 410
Largo, MD 20774
Tel: 301-304-6070/Cell: 240-472-6570
eking@erogerfinancial.com / www.erogerfinancial.com
Stock Indices:
| Dow Jones | 44,094 |
| S&P 500 | 6,204 |
| Nasdaq | 20,369 |
Bond Sector Yields:
| 2 Yr Treasury | 3.72% |
| 10 Yr Treasury | 4.24% |
| 10 Yr Municipal | 3.21% |
| High Yield | 6.80% |
YTD Market Returns:
| Dow Jones | 3.64% |
| S&P 500 | 5.50% |
| Nasdaq | 5.48% |
| MSCI-EAFE | 17.37% |
| MSCI-Europe | 20.67% |
| MSCI-Pacific | 11.15% |
| MSCI-Emg Mkt | 13.70% |
| US Agg Bond | 4.02% |
| US Corp Bond | 4.17% |
| US Gov’t Bond | 3.95% |
Commodity Prices:
| Gold | 3,319 |
| Silver | 36.32 |
| Oil (WTI) | 64.98 |
Currencies:
| Dollar / Euro | 1.17 |
| Dollar / Pound | 1.37 |
| Yen / Dollar | 144.61 |
| Canadian /Dollar | 0.73 |
Macro Overview
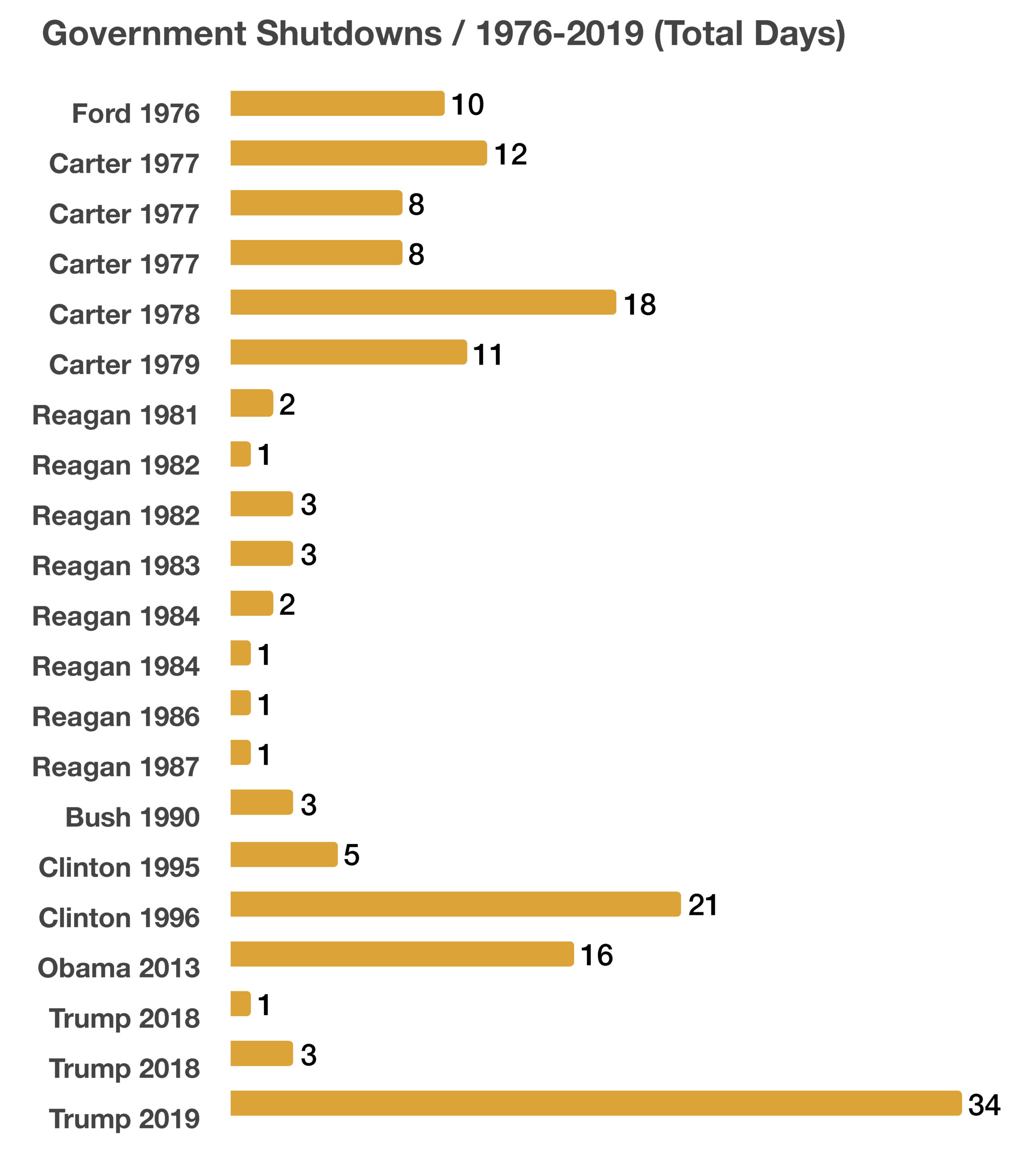
A federal government shutdown was averted on September 30th, when Congress voted to fund government operations until mid-November. Volatility in the financial markets increased during September, as uncertainty surrounding a resolution persisted. The possibility of a shutdown will evolve again in November, as Congress once again deliberates on the passage of the federal budget. Should a shutdown occur, the impact on the economy would initially be mild as previous shutdowns, and possibly expanding as millions of government workers go without salary. Private sector contractors would also be impacted with delayed payments, while consumer uncertainty hinders spending.
The federal government shutdown dilemma has increased the possibility of a credit downgrade by Moody’s, the last agency with a AAA rating on government debt. Credit agencies S&P and Fitch have already lowered their ratings on U.S. government debt to AA+, down from the top tier rating of AAA. Another downgrade is expected to make it more costly for the government to borrow funds and maintain already excessive debt levels. The last downgrade was on August 1st when Fitch lowered its rating to AA+ from AAA.
A shutdown of the federal government is expected to affect only government operations and payments that are not funded by permanent appropriations. Those funded by permanent appropriations such as the Postal Service, entitlement programs such as Social Security and Medicare, will not be affected. Other essential and critical departments and agencies of the government would also continue operations, such as the Defense Department and the Treasury Department. Scheduled debt payments such as on Treasury bills, notes and bonds would also continue to be made.
Relentless rising oil prices are hindering portions of the economy, inflicting rising costs on transportation, manufacturing, and food distribution. Equity analysts believe that some companies may see compressed earnings as lofty fuel costs continue to wear on operating expenses. Higher costs can eventually be passed on to consumers in the form of higher prices.
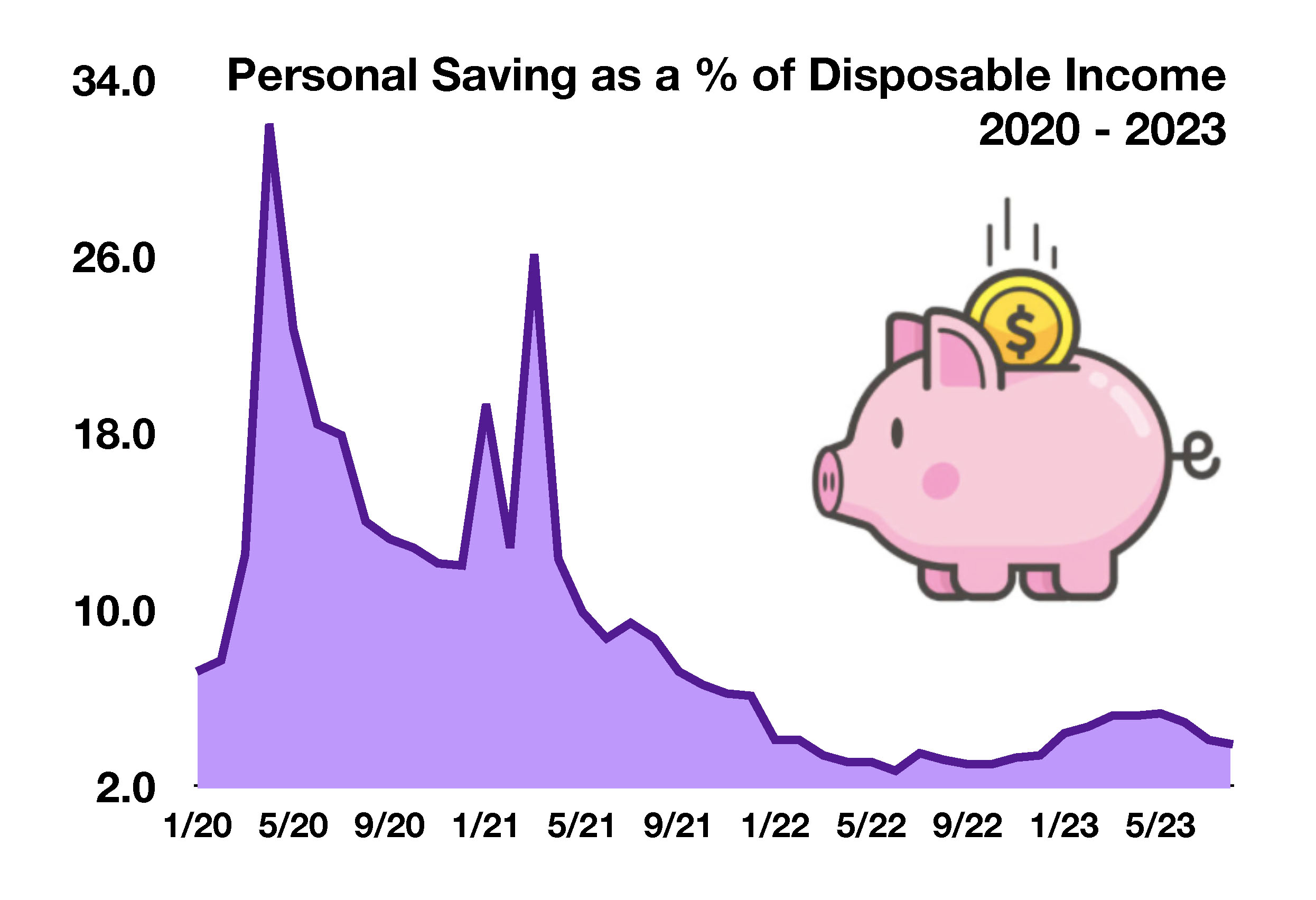
Medicare open enrollment is from October 15th to December 7th, allowing changes for existing medicare recipients and enrollments for new members. Any changes and new enrollments are effective January 1, 2024. The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) reports that there are currently over 65.7 million people enrolled in Medicare. (Sources: Social Security Administration, Medicare.gov, Treasury Dept., Federal Reserve)

 As the highways expanded to accommodate more traffic and heavier loads, roads and bridges have become integral components to the nation’s transportation system. Of the 117,483 bridges covering the nation’s highways, The Department of Transportation has identified over 5,230 as structurally deficient. The District of Columbia alone has over 16% of its highway bridges deemed structurally deficient.
As the highways expanded to accommodate more traffic and heavier loads, roads and bridges have become integral components to the nation’s transportation system. Of the 117,483 bridges covering the nation’s highways, The Department of Transportation has identified over 5,230 as structurally deficient. The District of Columbia alone has over 16% of its highway bridges deemed structurally deficient.