Joseph Schw
Stephen Dygos, CFP® 612.355.4364
Benjamin Wheeler, CFP® 612.355.4363
Paul Wilson 612.355.4366
www.sdwia.com
Stock Indices:
| Dow Jones | 44,094 |
| S&P 500 | 6,204 |
| Nasdaq | 20,369 |
Bond Sector Yields:
| 2 Yr Treasury | 3.72% |
| 10 Yr Treasury | 4.24% |
| 10 Yr Municipal | 3.21% |
| High Yield | 6.80% |
YTD Market Returns:
| Dow Jones | 3.64% |
| S&P 500 | 5.50% |
| Nasdaq | 5.48% |
| MSCI-EAFE | 17.37% |
| MSCI-Europe | 20.67% |
| MSCI-Pacific | 11.15% |
| MSCI-Emg Mkt | 13.70% |
| US Agg Bond | 4.02% |
| US Corp Bond | 4.17% |
| US Gov’t Bond | 3.95% |
Commodity Prices:
| Gold | 3,319 |
| Silver | 36.32 |
| Oil (WTI) | 64.98 |
Currencies:
| Dollar / Euro | 1.17 |
| Dollar / Pound | 1.37 |
| Yen / Dollar | 144.61 |
| Canadian /Dollar | 0.73 |
Macro Overview – April 2020
With the coronavirus continuing to wreak havoc on markets and economies worldwide, governments and businesses are confronting an unprecedented environment. In response, massive fiscal and monetary stimulus efforts put into motion by the administration and the Federal Reserve are expected to provide unparalleled economic stimulus.
The World Health Organization (WHO) declared the COVID-19 virus a pandemic on March 11th, sending global equities further down and ending the longest bull run in U.S. history. The 20% plus decline for all three major equity indices, from record highs set in mid-February, qualified the rapid descent as an end to the bull market that began in March 2009.
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) determined that the global economy has fallen into a recession, due to disrupted global supply chains and a drop in commerce induced by the virus outbreak. Economists believe that international markets may eventually rebound should governments around the world effectively mitigate contamination.
The $2.2 trillion stimulus plan passed by Congress, known as the Cares Act, was the largest in U.S. history, providing critical funds to small business owners and individuals nationwide. Massive federal borrowing will fund the program in the form of U.S. government debt issuance expected to exceed $2 trillion in short-term Treasury bills this year alone.
Many economists and market analysts view this pandemic as a health crisis at its core, not a financial crisis, which has preceded nearly all previous recessions. Atlanta Fed President Raphael Bostic said that “this is a public health crisis and different from a typical recession”. Dallas Fed President Robert Kaplan expressed some optimism by commenting “we’ve got a great chance to come out of this very strong”. Some view government restrictions and mandatory closures as the reason behind crippled businesses and the economic contraction, not the coronavirus itself.
It is too soon to determine as to what the overall impact will be to the multitude of industries and companies over the next few months. Globalization is in question as global commerce has dwindled due to supply chain constraints, along with varying rules and restrictions among countries involving cross-border transactions.
The Federal Reserve took unprecedented steps to stabilize bond markets and maintain liquidity following dramatic volatility amid continued uncertainty. The Fed committed to spend nearly a trillion dollars for the purchase of Treasury bonds, municipal bonds, corporate bonds and agency bonds in order to support the bond markets. The purchase strategy is reminiscent of Quantitative Easing (Q.E.), which was initially utilized during the 2008-2009 financial crisis.
As recession has become more of a probability, some economists are projecting a V-shaped recessionary environment, where asset prices may bounce back sooner rather than later in the second half of the year. Historically, the U.S. has never entered a recession with interest rates as low as they are now.
The Treasury Department and the IRS announced an extension of the tax filing deadline from April 15, 2020 to July 15, 2020. Taxpayers will be able to defer tax payments until July 15th, without any penalties and interest. The deferment applies to all taxpayers, including individuals, businesses, estates, and corporations.
A historical spike in unemployment claims of nearly 10 million was brought about by mass layoffs as governmental entities mandated business closures and restrictions across the country. The immense jump in unemployment claims over just two weeks may worsen, yet expected to be buffeted by funds targeted for the unemployed as a result of the $2.2 trillion stimulus plan. The plan also encourages small businesses to re-hire employees as conditions warrant.
Personal and business bankruptcies are expected to rise dramatically as a result of government mandated shutdowns, which have halted incomes for employers and employees across the country.
Sources: IMF, WHO, Fed, Treasury, IRS, Dept. of Labor
Equities Technically End Eleven Year Bull Market Run – Domestic Stock Market Overview
Equity markets experienced volatility in March not seen since the 1930s, with daily declines so sharp that rarely-used mechanisms to halt trading were activated by the exchanges on multiple occasions. The S&P 500 Index saw an average daily change of 5.2% in March, the most extreme volatility since November 1929.
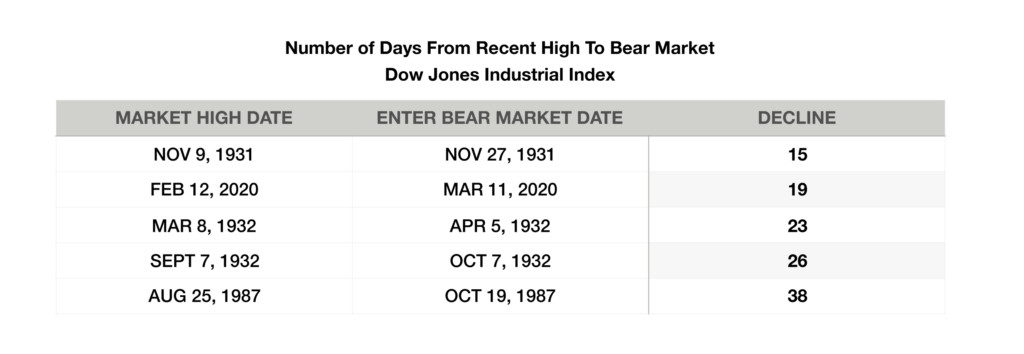
Stocks fell into bear market territory and then out of it in technically the shortest bear market in history. The last time the Dow Jones Index went from its bear market low to a bull market in only three days was in October 1931. Stocks had their worst quarter in years, with the S&P 500 Index losing 20% for the quarter ending March 31st, and the Dow Jones Industrial Index surrendering 23%. The bull market that began in March 2009, officially came to an end in March, after an 11-year run. The Dow Jones Industrial Index went from its high on Feb 12th to bear market territory in only19 trading sessions.
With massive stimulus plans now in place, the market’s recovery has become contingent on the virus timeline for containment and effective testing. Analysts expect that once the virus outbreak has abated, any remaining stimulus efforts by the administration and the Fed will continue to act as a stimulus for the markets.
Signs of resilience at the end of March suggest that equities may regain their footing sometime soon. Overall valuations on stocks have fallen to levels that warrant accumulation of certain companies and industries. Eyes will be on earnings and quarterly performance releases over the next few weeks, as analysts determine how much of an impact the pandemic has thus had.
Sources: S&P, Dow Jones, Bloomberg
Massive Stimulus Efforts Bring Yields To Historic Lows – Fixed Income Update
The Federal Reserve announced a reintroduction of its Quantitative Easing (QE) program to now include corporate bonds in addition to government agency and Treasury bonds. The program essentially entails the buying of an unlimited amount of bonds in the open market, thus stabilizing prices and volatile trading caused by a dislocation in the market. Intervention in the corporate bond market is an unprecedented action for the Federal Reserve, in addition to initiating programs to ensure sufficient access to credit for public and private entities such as cities, counties, municipalities, as well as corporations.
The incredible demand for short-term government bonds outstripped the supply of Treasury bills issued by the U.S. Treasury in mid-March. When demand exceeds supply by such an extent, short-term rates drop, in turn sending money market rates lower. Assets have been pouring into money market funds as market conditions created a rush away from volatility.
The Fed reduced its key lending rate to 0%-0.25% in March and announced that it would begin buying $700 billion in Treasury and mortgage bonds immediately. The Federal Reserve announced that it would also be buying selected corporate bonds and municipal securities in the open market in order to help stabilize broad fixed income sectors. Buying corporate and municipal bonds deviates from traditional Fed policies as a result of the current extraordinary conditions.
Credit rating firm Fitch, mentioned that its AAA credit rating on U.S. government debt is at risk of being downgraded due to the spontaneous rise in the country’s deficit and debt level brought upon by the virus crisis. Lower credit ratings for government debt tend to eventually make it more costly for a nation to borrow funds.
Credit markets also experienced dislocation in March, a term used to describe that bonds aren’t trading as they usually do, exhibiting erratic valuations and liquidity constraints.
Some analysts view the increase in long-term Treasury yields as an indicator that economic growth will eventually return, albeit, with some inflationary pressures hinged to it. Other analysts see higher Treasury yields resulting from newly issued government debt along with the already excessive fiscal deficit.
Sources: Federal Reserve, Treasury, Fitch
$2.2 Trillion Stimulus Plan Highlights For Individuals & Small Businesses
The passage of the $2.2 trillion stimulus plan, known as the Coronavirus Aid, Relief and Economic Security Act (Cares Act), provides critical funds to various sectors of the economy in the form of payments, tax breaks, loans, and subsidies to individuals and small businesses nationwide.
As the largest economic relief package in U.S. history, the $2.2 trillion stimulus plan equates to 9% of GDP, which is roughly $21 trillion. The primary goal of the stimulus program is to alleviate personal and business bankruptcies brought about by government mandated shutdowns and restrictions.
Stimulus Payments
$1,200 for each eligible taxpayer earning up $75,000. Joint filers will receive $2,400 earning up to $150,000, based on 2019 tax returns or 2018 if not already filed. Stimulus payment amounts decline as income levels rise. For filers with income above those amounts, the payment amount is reduced by $5 for each $100 above the $75,000/$150,000 thresholds. Single filers with income exceeding $99,000 and $198,000 for joint filers with no children are not eligible. Social Security recipients who are otherwise not required to file a tax return are also eligible and will not be required to file a return.
Unemployment
An additional $600 per week for four months for unemployment, in addition to any state unemployment benefit.
Retirement Plan Withdrawals
Withdrawals from IRAs and company sponsored retirement plans such as 401k plans will not be imposed the 10% penalty up to $100,000 in distributions. The waiver applies to those who have been diagnosed with COVID-19 or have experienced financial hardship related to the virus through December 31, 2020. Distributions will still be taxable as income, but be spread out over three years.
401k Loans
The maximum 401k loan amount of $50,000 has been raised to $100,000 to accommodate larger loan needs. Loan limitations are based on 50% of a 401k account balance.
RMDs
Required Minimum Distributions (RMDs) on retirement accounts including IRAs have been waived for tax year 2020.
Mortgage Forbearance
Federally backed mortgage holders can forgo payments for six months under a forbearance program with no penalties or fees. A mortgage holder must be affected by COVID-19 and have approval from the lender.
Forecloses
All foreclosure proceedings are halted until May 18, 2020.
Student Loans
All federally-owned student loans will impose a 0% interest rate until September 30, 2020. Borrowers may also delay payments until September 30, 2020 via forbearance.
Paycheck Protection Program For Small Businesses
Lends up to $10 million to small businesses with fewer than 500 employees through the SBA. The allowable loan amount is calculated based on a company’s average monthly payroll. The loan may be considered a grant since loans are expected to be forgiven if the funds are used for expenses such as payroll, mortgage interest payments, rent, and utilities.
Sources: IRS; irs.gov/newsroom/economic-impact-payments, TaxPolicyCenter
IRS Tax Filing Deadline Extended To July 15th – Tax Policy
The IRS has extended the tax filing and payment deadline from April 15, 2020 to July 15, 2020. The new extension deadline applies to individuals, fiduciaries (estate and trusts), small business owners, and corporations. Individuals do not need to be infected by the coronavirus or subject to quarantine in order to have the July 15th extension apply.
Taxpayers are also able to defer federal income tax payments and quarterly estimates due on April 15, 2020, to July 15, 2020, without penalties and interest, regardless of the amount owed. The deferment applies to all taxpayers, including individuals, trusts and estates, corporations and other non-corporate tax filers in addition to those who pay self-employment tax. For individuals contributing to an IRA or IRA Roth, an HSA or MSA, the deadline of July 15th applies.
There is no form required or need to contact the IRS in order to have the July 15 deadline honored. The traditional tax filing date for extensions of October 15th remains the same. The IRS does urge taxpayers due a tax refund to apply sooner than the deadline in order to receive a refund check sooner.
Source: IRS; irs.gov/coronavirus, TaxPolicyCenter