Stock Indices:
| Dow Jones | 40,669 |
| S&P 500 | 5,569 |
| Nasdaq | 17,446 |
Bond Sector Yields:
| 2 Yr Treasury | 3.60% |
| 10 Yr Treasury | 4.17% |
| 10 Yr Municipal | 3.36% |
| High Yield | 7.69% |
YTD Market Returns:
| Dow Jones | -4.41% |
| S&P 500 | -5.31% |
| Nasdaq | -9.65% |
| MSCI-EAFE | 12.00% |
| MSCI-Europe | 15.70% |
| MSCI-Pacific | 5.80% |
| MSCI-Emg Mkt | 4.40% |
| US Agg Bond | 3.18% |
| US Corp Bond | 2.27% |
| US Gov’t Bond | 3.13% |
Commodity Prices:
| Gold | 3,298 |
| Silver | 32.78 |
| Oil (WTI) | 58.22 |
Currencies:
| Dollar / Euro | 1.13 |
| Dollar / Pound | 1.34 |
| Yen / Dollar | 142.35 |
| Canadian /Dollar | 0.72 |
Macro Overview
The prospect of resurgent inflation is a growing concern for global markets. Some economists project that current inflationary pressures may be transitory, while others contend that higher prices may be long-lasting and have a significant impact on global economic outlook.
A rising fiscal deficit, along with increasing levels of federal debt, are prompting the current administration to explore the most significant tax hikes since 1993. Tax increases are being discussed for corporations, businesses structured as pass-through entities, estate taxes, and capital gains.
Optimism regarding a third round of stimulus payments and rising vaccination rates fueled equity markets in March as a nascent economic revitalization took hold. Major equity indices ended the quarter positively as companies experienced a resurgence in consumer activity and sales.
The pandemic brought modifications to business models throughout numerous industries, many of which are passing along higher costs to consumers. Some of the higher cost trends are not necessarily being recognized by government inflation gauges and not accounted for in economic forecasts. The suggestion that inflationary pressures are only temporary is under intense scrutiny as a growing number of businesses are expected to make pricing changes permanent.
The IRS announced that it is extending the tax filing deadline to May 17th, allowing tax payers more time to assess the effects of COVID-related changes for individual and small business filers. With the IRS extending the deadline, nearly all states will likely follow suit and extend the tax deadline to May 17th as well, although most states are maintaining the due date of April 15th for estimated tax payments. In addition to stimulus payments, the $1.9 trillion bill passed in March, called the American Rescue Plan Act of 2021, will provide an exemption on taxes owed on unemployment benefits up to $10,200. The IRS communicated that automatic refunds would be issued to those who have already filed their 2020 taxes and paid taxes on unemployment received last year.
A $2.25 trillion infrastructure plan introduced by the administration is expected to focus on transportation, clean water, high-speed broadband, and manufacturing. An increase in corporate taxes is the primary source of funding for the proposed plan.
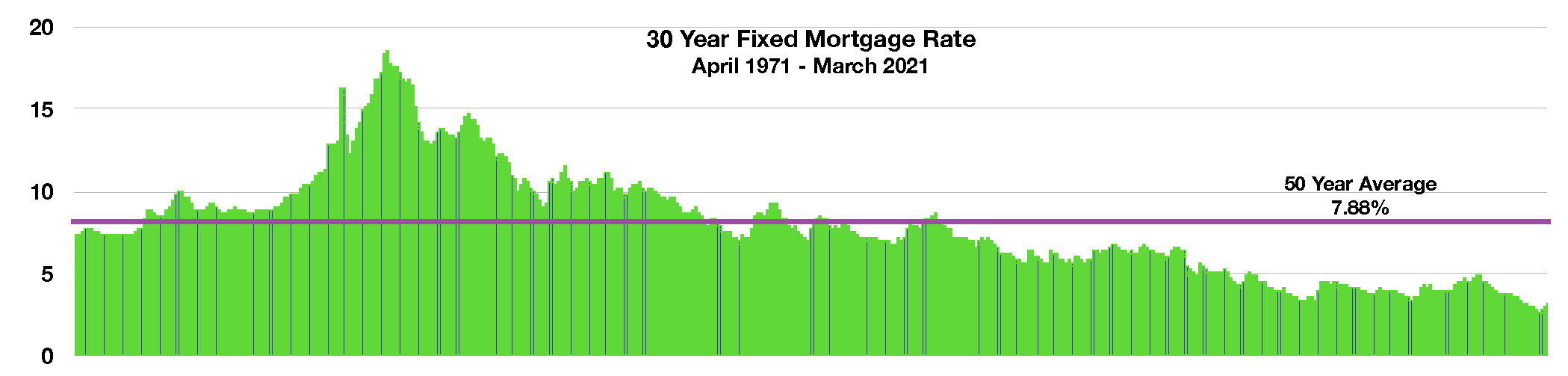
A rapid rise in mortgage rates since the beginning of the year led to a slowdown on refinances nationwide. The average 30-year fixed rate mortgage reached its highest level in over nine months at 3.17% as of March 25th, yet remains near historical lows relative to the 50-year average of 7.88% for a 30-year fixed mortgage.
Identified mutations of the COVID-19 virus raised concerns about the spread of a variant known to be more transmissible than the initial virus, prompting the CDC to caution the public about relaxing preventive measures.
Sources: IRS, Federal Reserve, CDC, Congress.gov