Michael McCormick
5 West Mendenhall, Ste 202 | Bozeman, MT 59715
406.920.1682 mike@mccormickfinancialadvisors.com
Sustainable Income Planning | Investments | Retirement
Stock Indices:
| Dow Jones | 40,669 |
| S&P 500 | 5,569 |
| Nasdaq | 17,446 |
Bond Sector Yields:
| 2 Yr Treasury | 3.60% |
| 10 Yr Treasury | 4.17% |
| 10 Yr Municipal | 3.36% |
| High Yield | 7.69% |
YTD Market Returns:
| Dow Jones | -4.41% |
| S&P 500 | -5.31% |
| Nasdaq | -9.65% |
| MSCI-EAFE | 12.00% |
| MSCI-Europe | 15.70% |
| MSCI-Pacific | 5.80% |
| MSCI-Emg Mkt | 4.40% |
| US Agg Bond | 3.18% |
| US Corp Bond | 2.27% |
| US Gov’t Bond | 3.13% |
Commodity Prices:
| Gold | 3,298 |
| Silver | 32.78 |
| Oil (WTI) | 58.22 |
Currencies:
| Dollar / Euro | 1.13 |
| Dollar / Pound | 1.34 |
| Yen / Dollar | 142.35 |
| Canadian /Dollar | 0.72 |
Macro Overview
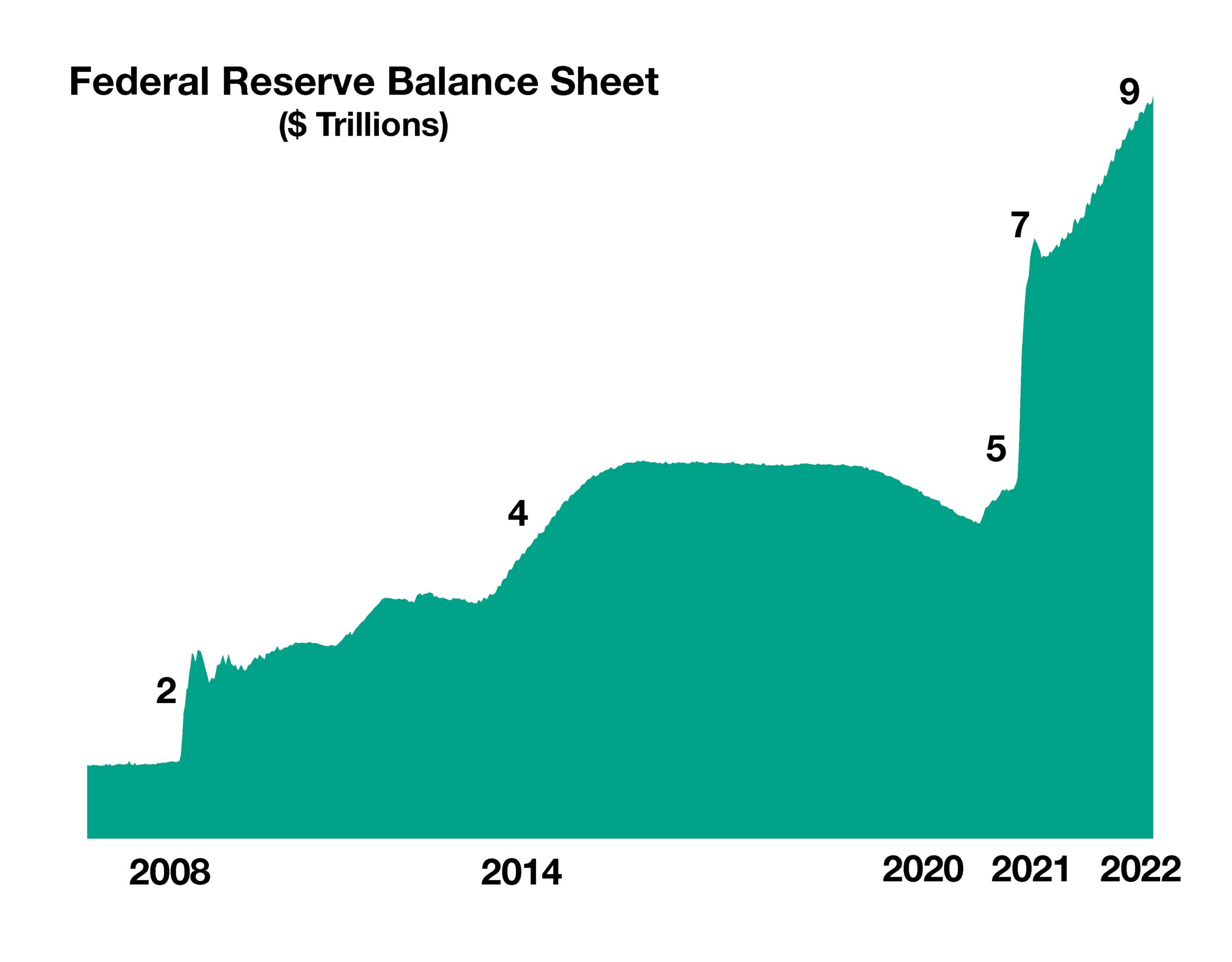
Market dynamics are shifting as the Federal Reserve outlines its execution of ending monetary stimulus in order to squash inflationary pressures.
Analysts and economists are expecting market volatility to continue as the Federal Reserve prepares to embark on its interest rate increase initiative. Some believe that the Fed will successfully pull off a series of four possible rate increases this year culminating in a “soft landing” whereas a rise in rates to control inflation doesn’t stifle economic expansion.
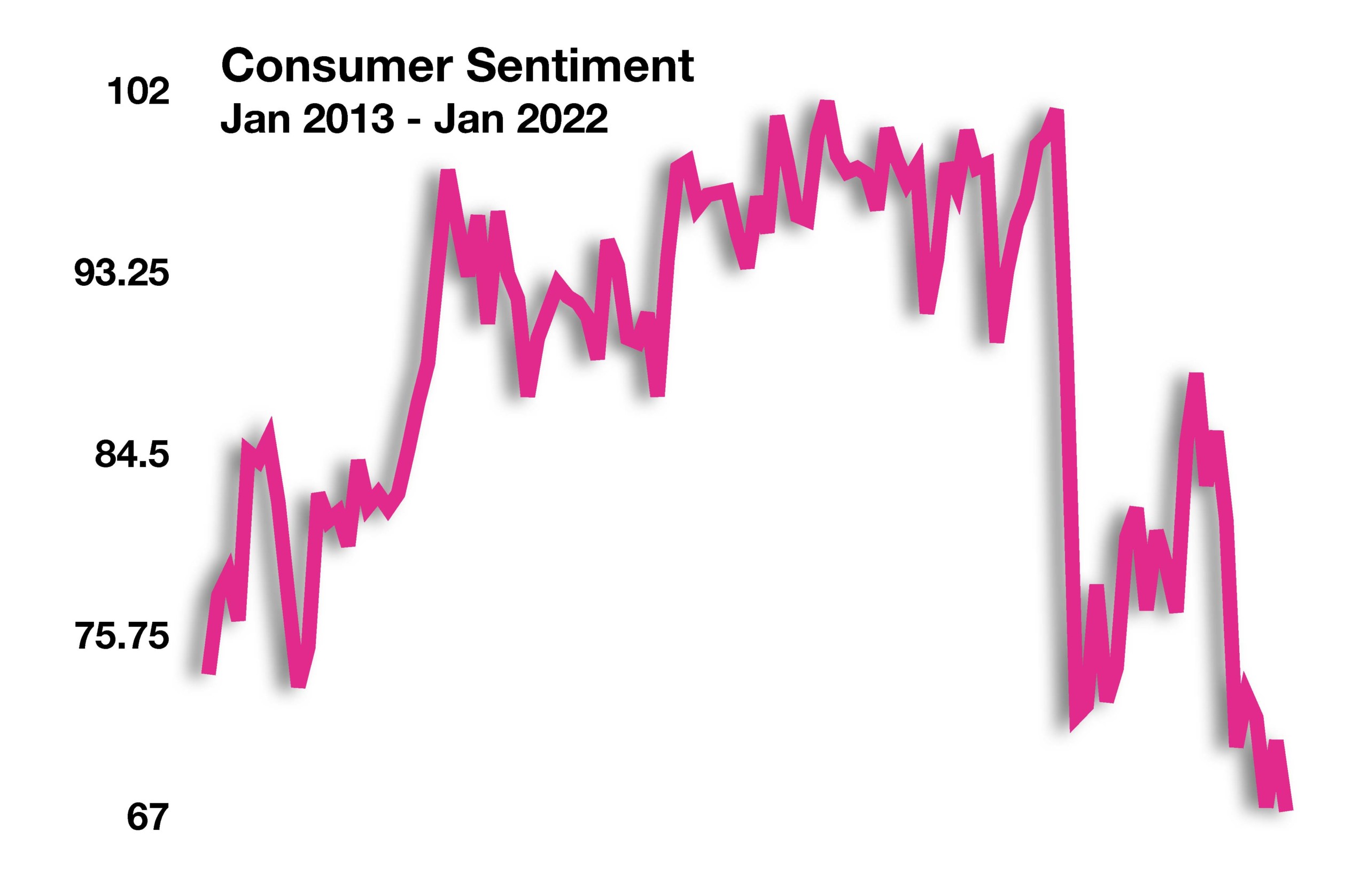
Inflation reached the highest level in 40 years, annualizing 7% at the end of 2021. Several analysts and economists believe that inflation may be peaking and may actually reverse course in coming months. It is also plausible that the Fed’s rush to raise rates simultaneously as pandemic stimulus funds have evaporated, may slow economic growth more than anticipated and ease inflation precipitously.
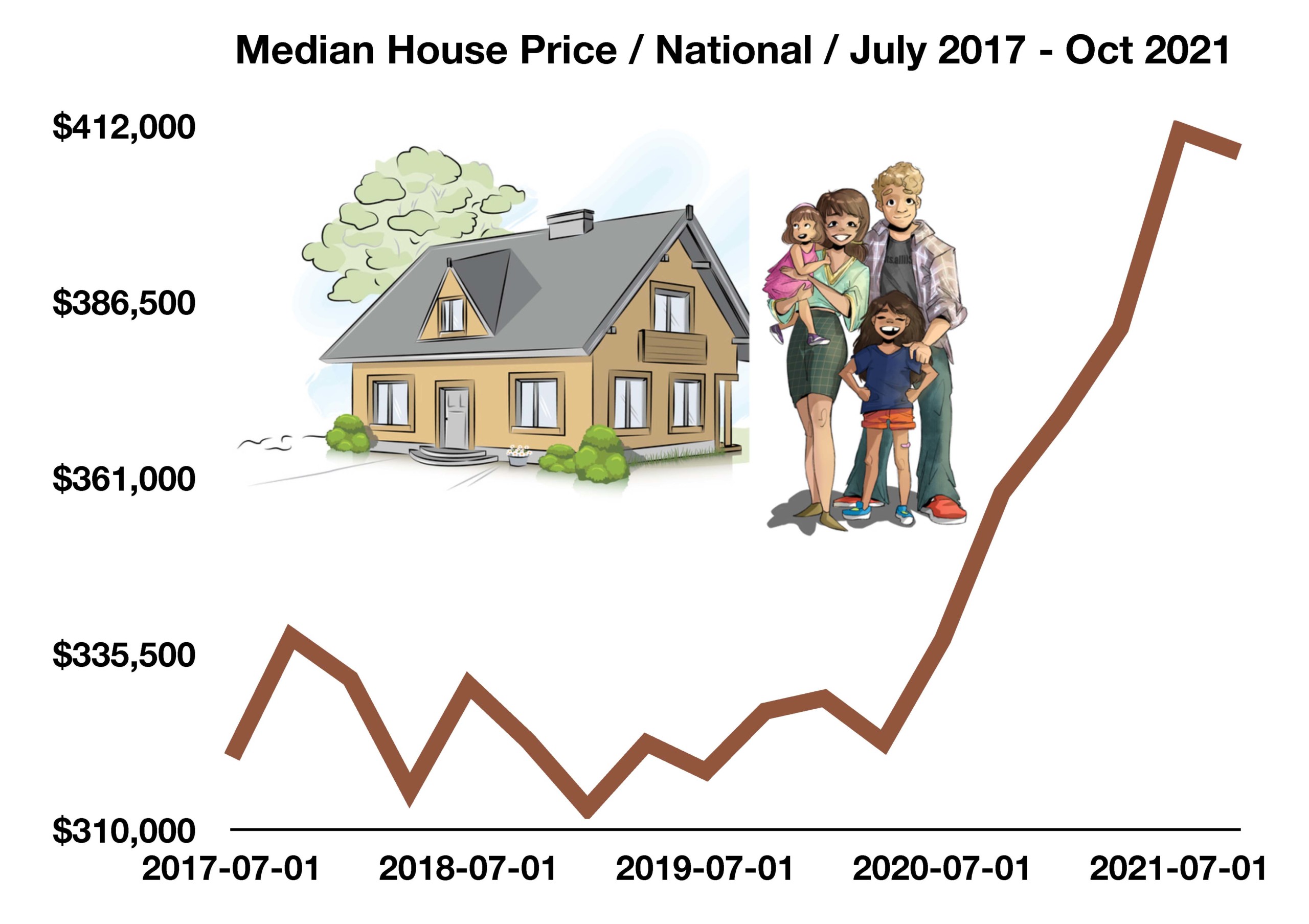
Supply constraints are still prevalent throughout the country, caused by multiple factors that neither the administration nor the Federal Reserve can alleviate. As higher prices evolve from the constraints, consumers modify spending behavior in order to accommodate inflationary tensions. The Atlanta Fed GDPNow model projects a substantial pullback in retail spending as consumers exhaust all remaining stimulus funds and minimize expenditures on costly discretionary goods.
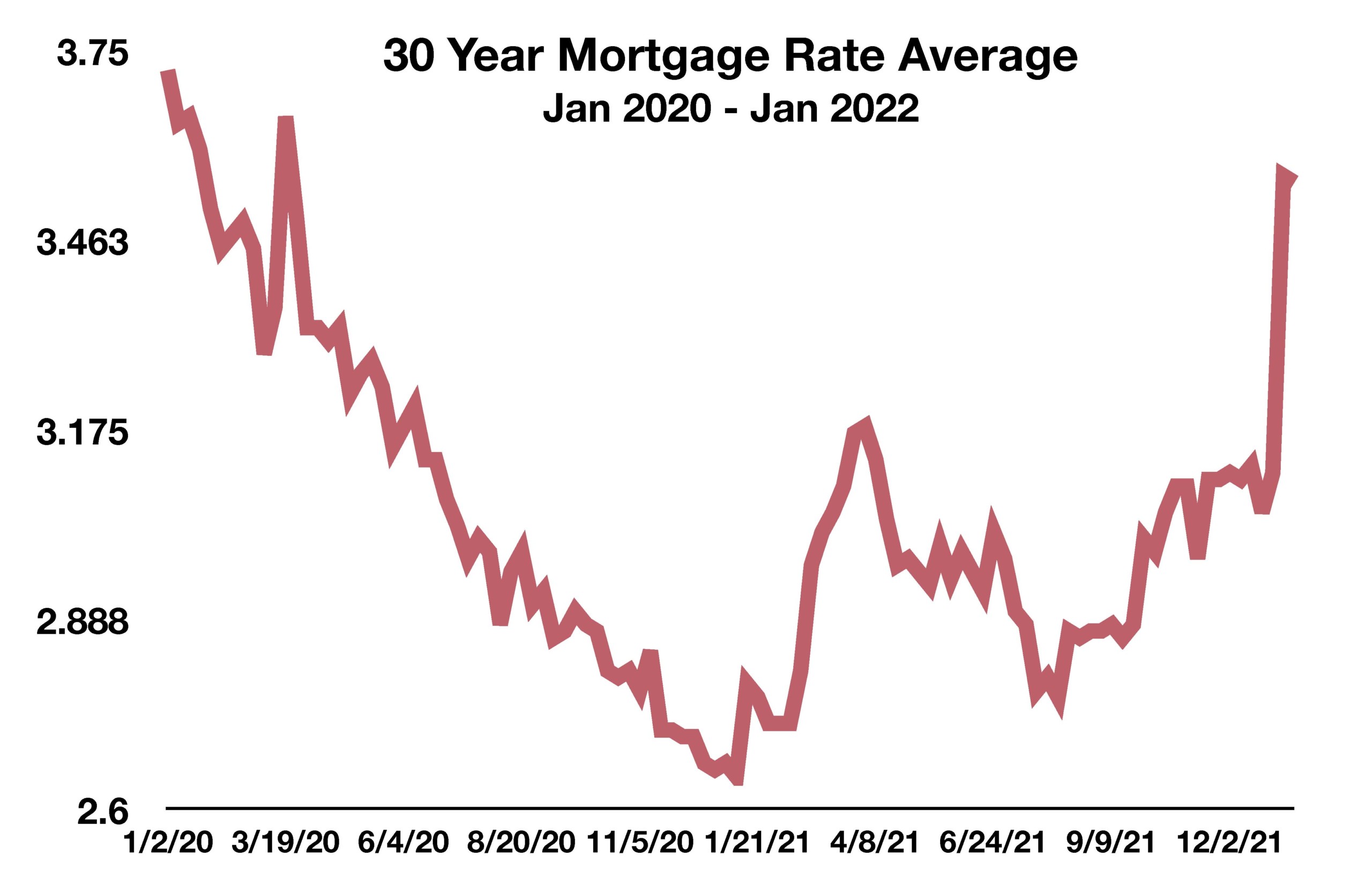
Financial market volatility intensified in January, as geopolitical tensions coupled with expectations of an imminent Fed rate hike drove equity and bond prices in extreme directions. Major equity and fixed income indices saw price declines in January.
Crude oil prices posted their strongest January in decades as expanding global demand and limited supply propelled prices higher. Rising oil prices have also translated into rising gasoline prices nationwide, with some analysts expecting even higher prices heading into the summer months.
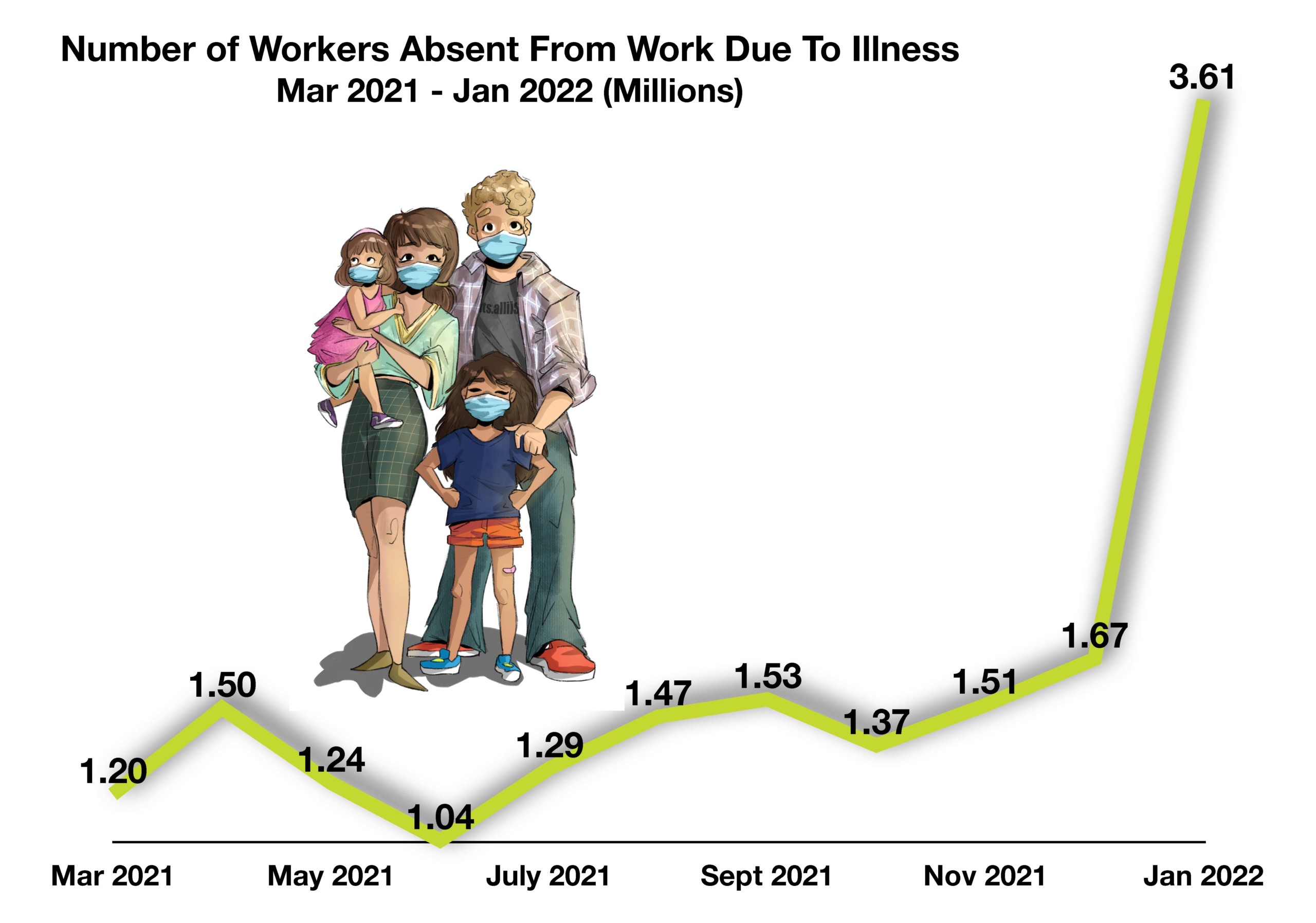
The Census Bureau, via its Household Pulse Survey, found that over 40% of unemployed individuals blame Covid related reasons for their unemployment. The same survey also identified that there were over 3.5 million workers absent from work in January due to illness, a record number. Labor market data has become a focal point for the Federal Reserve and financial markets, as distortions surrounding what the data is relaying about the actual economic health of the economy. (Sources: Fed, Labor Dept., www.census.gov/data/experimental-data-products/household-pulse-survey.html)
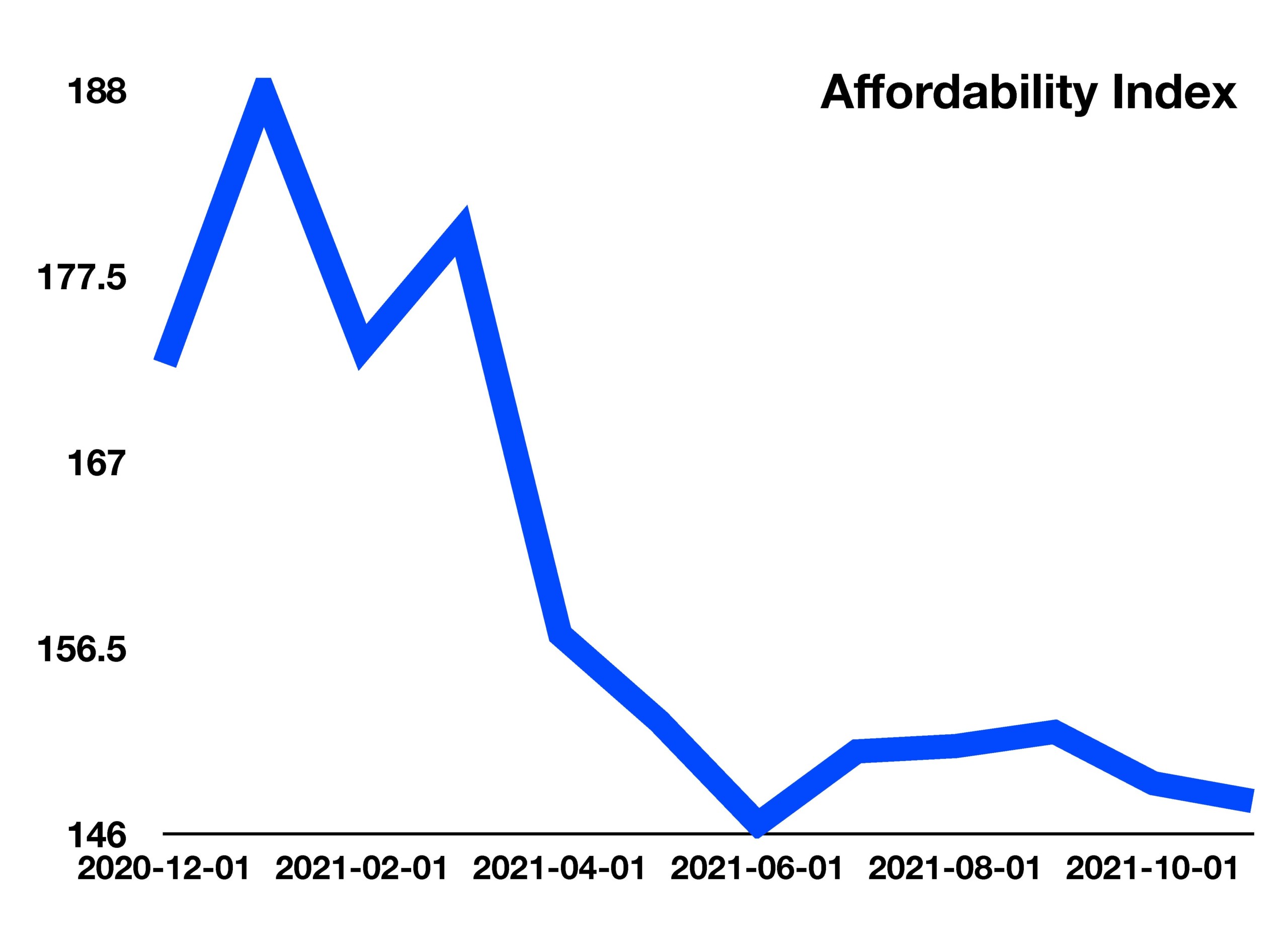
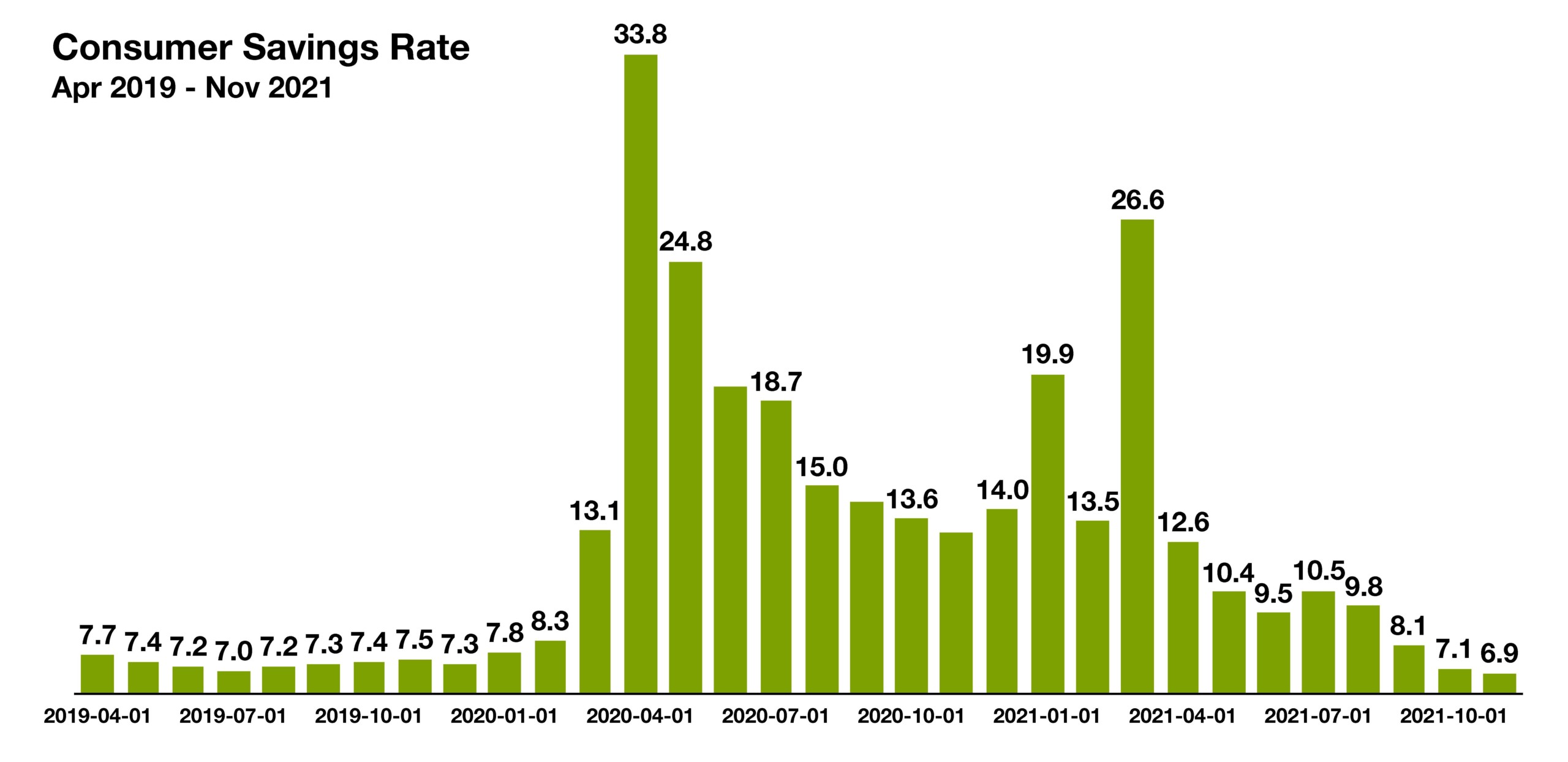 The most recent data show that the savings rate dropped to 6.9 percent in November 2021, lower than where it stood at roughly 7.5 percent before the pandemic began.
The most recent data show that the savings rate dropped to 6.9 percent in November 2021, lower than where it stood at roughly 7.5 percent before the pandemic began.