Stock Indices:
| Dow Jones | 46,397 |
| S&P 500 | 6,688 |
| Nasdaq | 22,660 |
Bond Sector Yields:
| 2 Yr Treasury | 3.60% |
| 10 Yr Treasury | 4.16% |
| 10 Yr Municipal | 2.92% |
| High Yield | 6.56% |
YTD Market Returns:
| Dow Jones | 9.06% |
| S&P 500 | 13.72% |
| Nasdaq | 17.34% |
| MSCI-EAFE | 22.34% |
| MSCI-Europe | 24.64% |
| MSCI-Pacific | 17.97% |
| MSCI-Emg Mkt | 25.16% |
| US Agg Bond | 6.13% |
| US Corp Bond | 6.88% |
| US Gov’t Bond | 5.93% |
Commodity Prices:
| Gold | 3,882 |
| Silver | 46.77 |
| Oil (WTI) | 62.52 |
Currencies:
| Dollar / Euro | 1.17 |
| Dollar / Pound | 1.34 |
| Yen / Dollar | 148.71 |
| Canadian /Dollar | 0.71 |
Macro Overview
The most recent inflation data released revealed an 8.5% annual increase, yet came in below what many analysts had expected. A consensus is forming, among economists and analysts, that inflation may be peaking. The hope is that the Fed may ease its rapid rate rise trajectory should inflation actually be slowing.
The Russian invasion of Ukraine has now entered its third month with no sign of a compromise, along with a list of international sanctions which continue to expand and impose economic duress on the Russian economy. The situation, meanwhile, continues to exasperate global supply chain constraints producing material and commodity shortages throughout various industries.
An increase in Covid cases throughout China is hampering manufacturing and distribution for various industries throughout the country delaying the shipment of finished goods to the United States as well as other countries, enhancing supply side constraints.
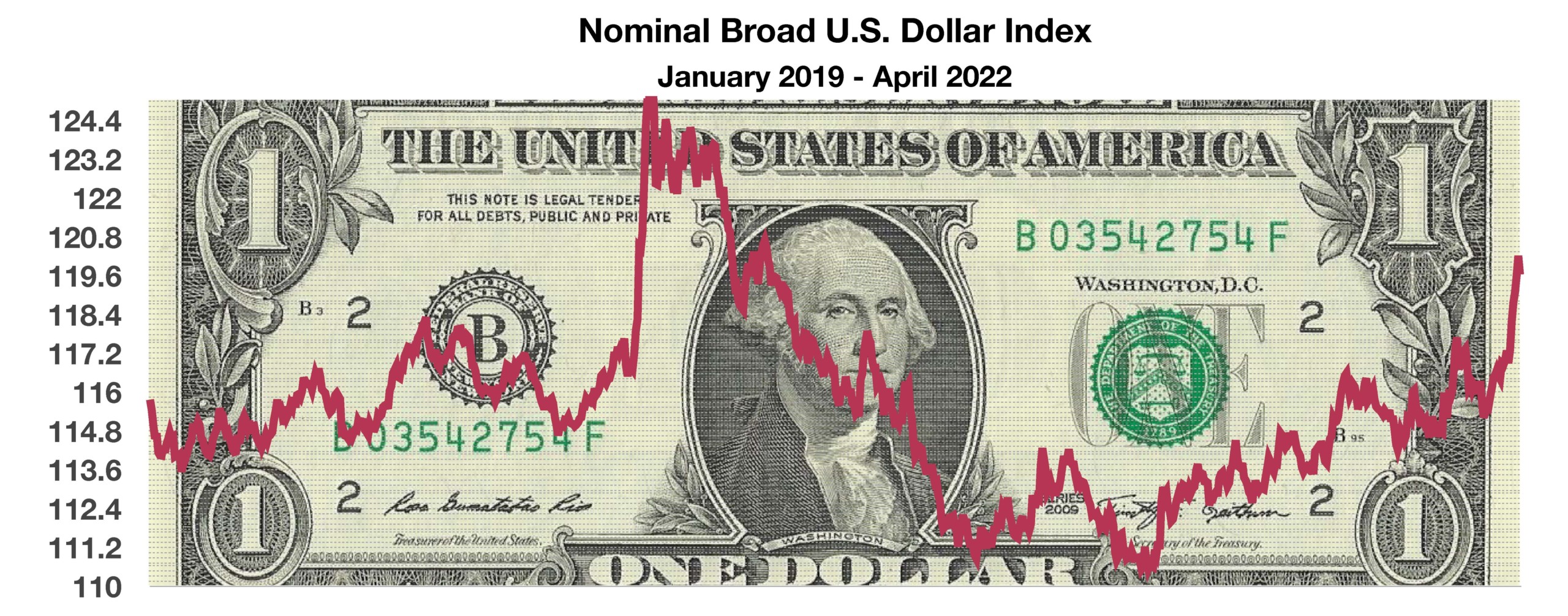
The U.S. dollar has risen nearly 7% for the year versus other major currencies, making imports less expensive for U.S. consumers and helping to alleviate inflationary pressures. Meanwhile, the Russian invasion of Ukraine has devalued the euro creating inflationary pressures throughout Europe, which is a substantial importer of petroleum & natural gas.
Employment costs for companies rose in the latest release from the Bureau of Labor Statistics, showing an increase in expenses related to wages and benefits for both government and private sector jobs. Rising employment costs pose a challenge to companies as they either pass along higher costs to consumers or have their margins reduced. Rising employment costs contribute to broad inflationary pressures.
Global growth forecasts were reduced by the IMF and the World Bank, due to geopolitical tensions arising from the Russian invasion, which continues to inflame supply chain issues worldwide and foster inflation. European companies are at additional risks if demand from China and the U.S. falters due to an economic slowdown.
Russian energy companies are reluctant to cut further fuel sales to European countries because a loss of revenue would threaten the stability of the Russian energy industry. Roughly 70% of Russian exports are energy products such as natural gas and petroleum, while about 8% of U.S. exports are energy related. Russia’s reliance on energy exports is critical for the integrity of the country’s economy. The halt of Russian natural gas to various European countries is expected to benefit U.S. energy companies as U.S. shipments of LNG (Liquid Natural Gas) to Europe are estimated to increase over 60% in 2022 relative to 2021.
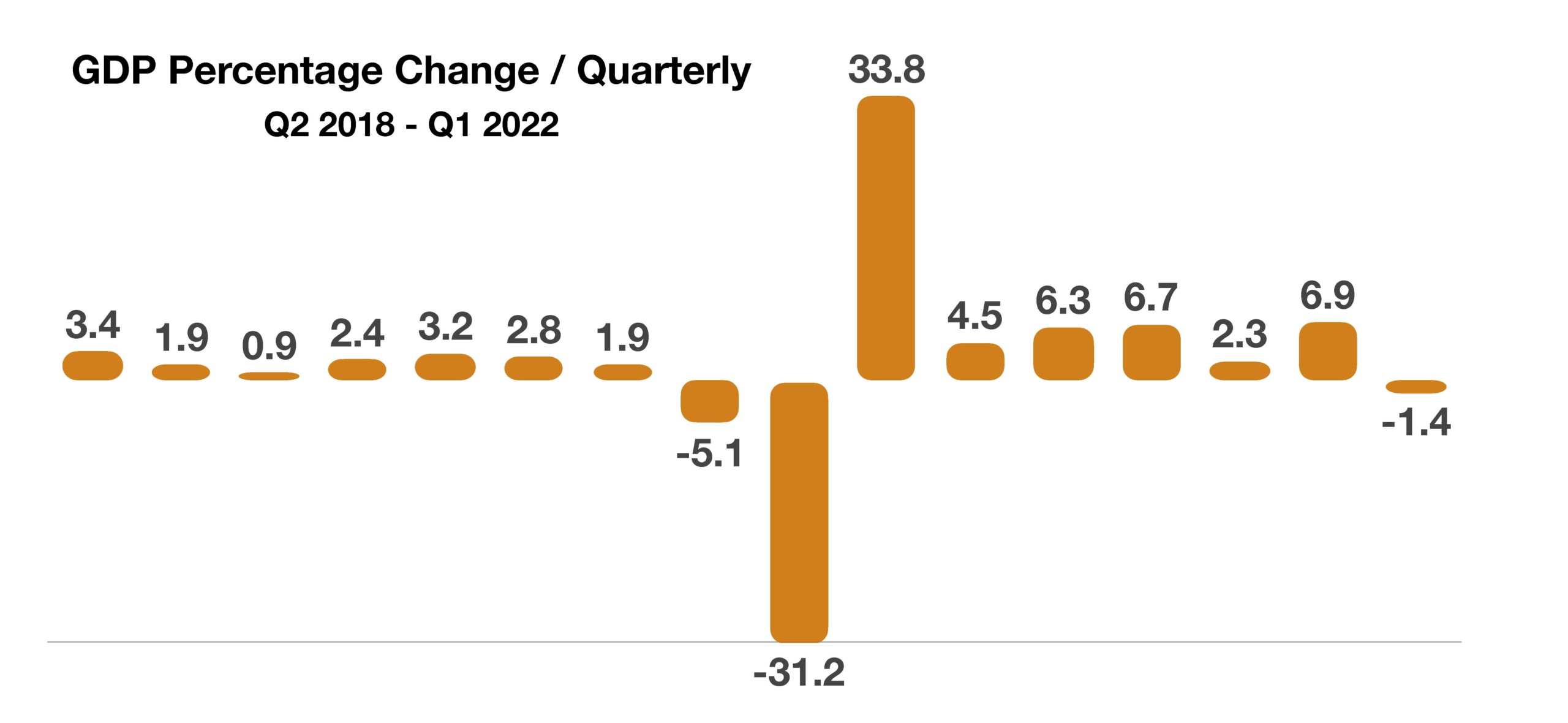
Numerous analysts are expecting the housing market to start cooling off relatively soon due to rising mortgage rates and slowing real wage growth. The concern is that as housing slows, so might GDP, as the housing industry represents roughly 20% of the nation’s economic growth.
Sources: EIA, Labor Dept., Federal Reserve, BLS, IMF, World Bank
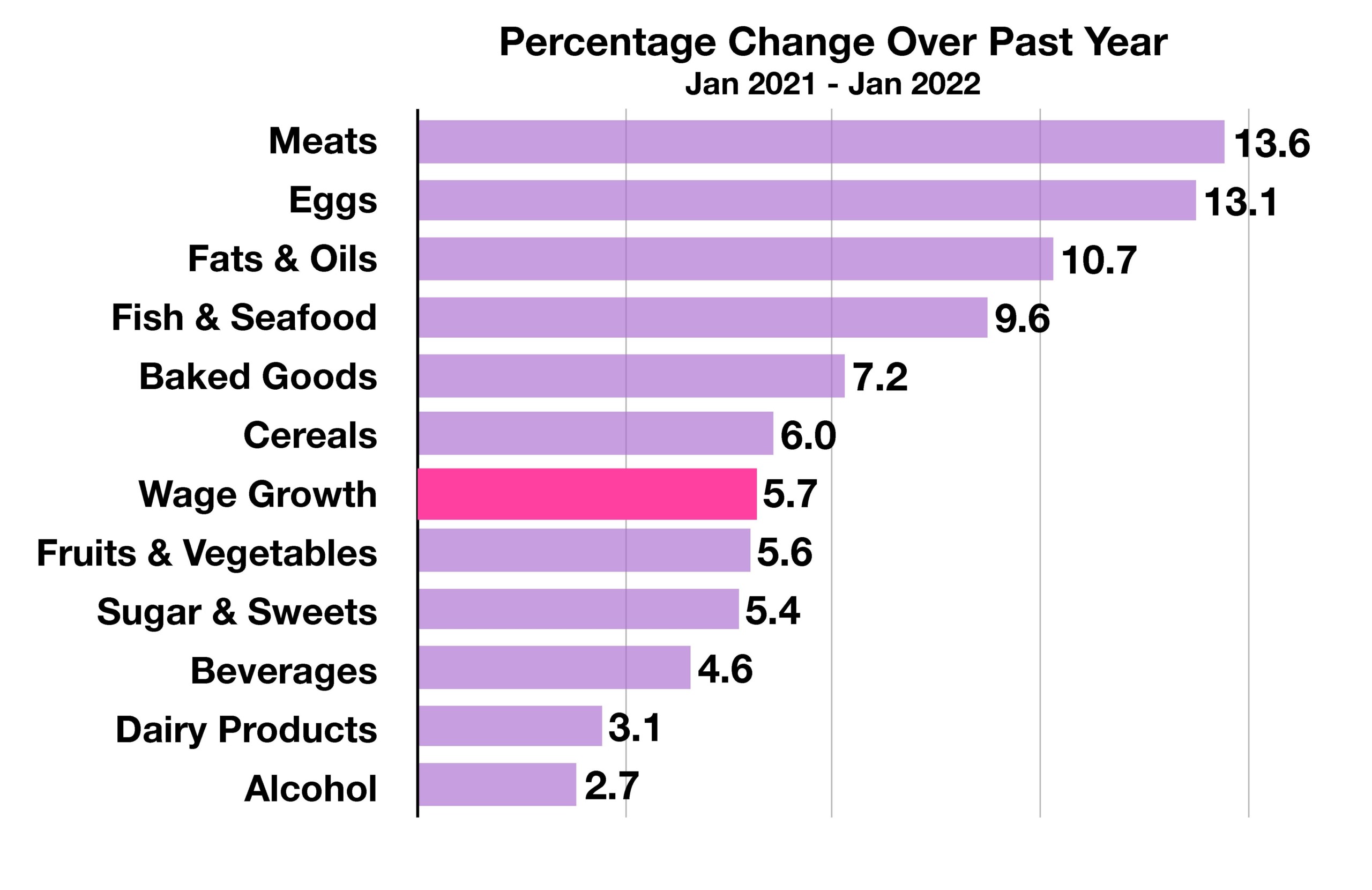
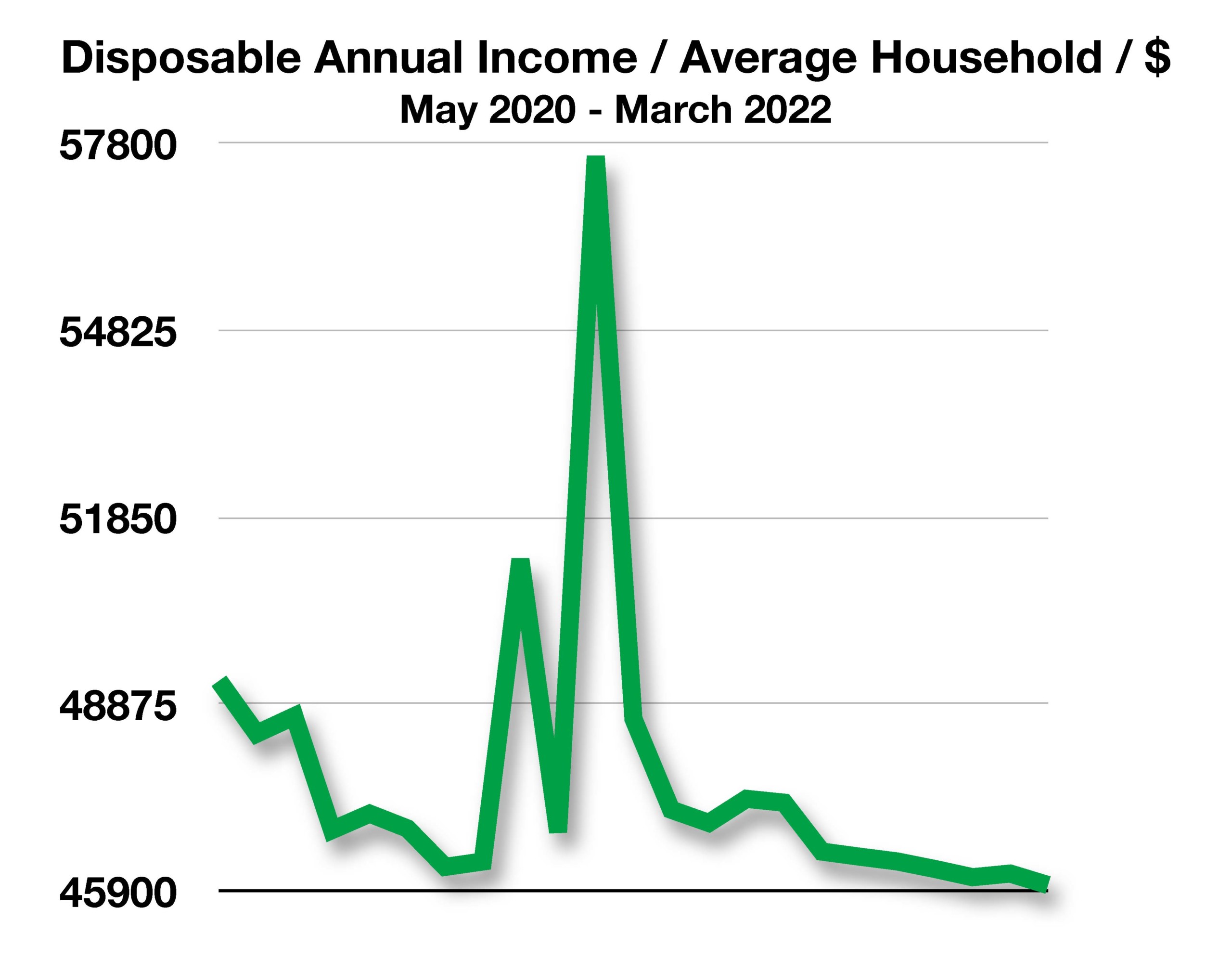
 Economists view a number of factors affecting growth in the U.S. economy, with no sole reason for any possible slowdown. Contributing to a pullback in expansion include exhaustion of pandemic relief funds, rising interest rates, inflation, lower disposable income, and uncertainty surrounding Covid infections. (Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics, Bloomberg)
Economists view a number of factors affecting growth in the U.S. economy, with no sole reason for any possible slowdown. Contributing to a pullback in expansion include exhaustion of pandemic relief funds, rising interest rates, inflation, lower disposable income, and uncertainty surrounding Covid infections. (Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics, Bloomberg)