Stock Indices:
| Dow Jones | 42,330 |
| S&P 500 | 5,762 |
| Nasdaq | 18,189 |
Bond Sector Yields:
| 2 Yr Treasury | 3.66% |
| 10 Yr Treasury | 3.81% |
| 10 Yr Municipal | 2.63% |
| High Yield | 6.66% |
YTD Market Returns:
| Dow Jones | 12.31% |
| S&P 500 | 20.81% |
| Nasdaq | 21.17% |
| MSCI-EAFE | 12.90% |
| MSCI-Europe | 12.10% |
| MSCI-Pacific | 13.80% |
| MSCI-Emg Mkt | 16.80% |
| US Agg Bond | 4.44% |
| US Corp Bond | 5.32% |
| US Gov’t Bond | 4.39% |
Commodity Prices:
| Gold | 2,657 |
| Silver | 31.48 |
| Oil (WTI) | 68.27 |
Currencies:
| Dollar / Euro | 1.11 |
| Dollar / Pound | 1.33 |
| Yen / Dollar | 142.21 |
| Canadian /Dollar | 0.73 |

Equity markets defied the historically negative month of October with equity indices moving higher despite ongoing trade dispute uncertainty and growing concerns of global economic headwinds.
Major domestic and international equity indices rose in sync as interest rates remained low worldwide, driving assets into stocks. Monetary policy that prompted rate cuts by central banks around the world are expected to provide stimulus and bolster global growth as the cost to borrow remains low.
Some concerns do exist surrounding a global economic slowdown, with attention on economic data becoming a focal point for analysts and economists. U.S. equities have continued to perform as a result of an accommodative monetary policy driven by the Federal Reserve and consistent consumer demand which have buoyed stock valuations.
Trade talks between the U.S. and China have continued to roil markets as inconsistent messages regarding any progress on trade discussions have not yielded any formal trade agreements. The ongoing trade dispute has brought about revisions to economic growth estimates by economists and international organizations such as the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and the World Trade Bank.
Bond yields rose in October, a possible indication that growth dynamics are propelling some prices and interest rates higher. Economists view a slight rise in rates optimistically due to healthy economic forces driving expansion. Treasury bond yields saw modest increases in October, with the 10-year Treasury yield rising to 1.69% on October 31st from 1.68% on September 30th.
The Federal Reserve cut its key interest rate for the third time this year. The most recent cut in late October was preceded by two cuts earlier in the year, the first in July and the second in September. The Fed hinted that no further rate cuts were anticipated unless weaker economic data warranted additional cuts.
The Treasury and the Federal Reserve are closely monitoring the possibility of year end volatility when banks are hesitant to part with cash reserves, which affects money markets. Short-term rates briefly spiked in September as the cost for banks to borrow cash against Treasuries jumped. Banks actively participate in Fed driven strategies that indirectly affect short-term rates and liquidity in the bond markets.
Following several failed attempts to formally extract Great Britain from the European Union (EU), also known as Brexit, the prime minister of Great Britain has given the vote back to the people of Great Britain with an election on December 12th. British voters originally voted on exiting the EU in 2016, but with no formal agreement ever having been reached between the British government and the EU. The vote is expected to garner enormous attention from other EU countries considering an EU exit vote.
Sources: Federal Reserve, U.S. Treasury, EuroStat
 Stock Indices Move Higher In October – Global Equity Review
Stock Indices Move Higher In October – Global Equity Review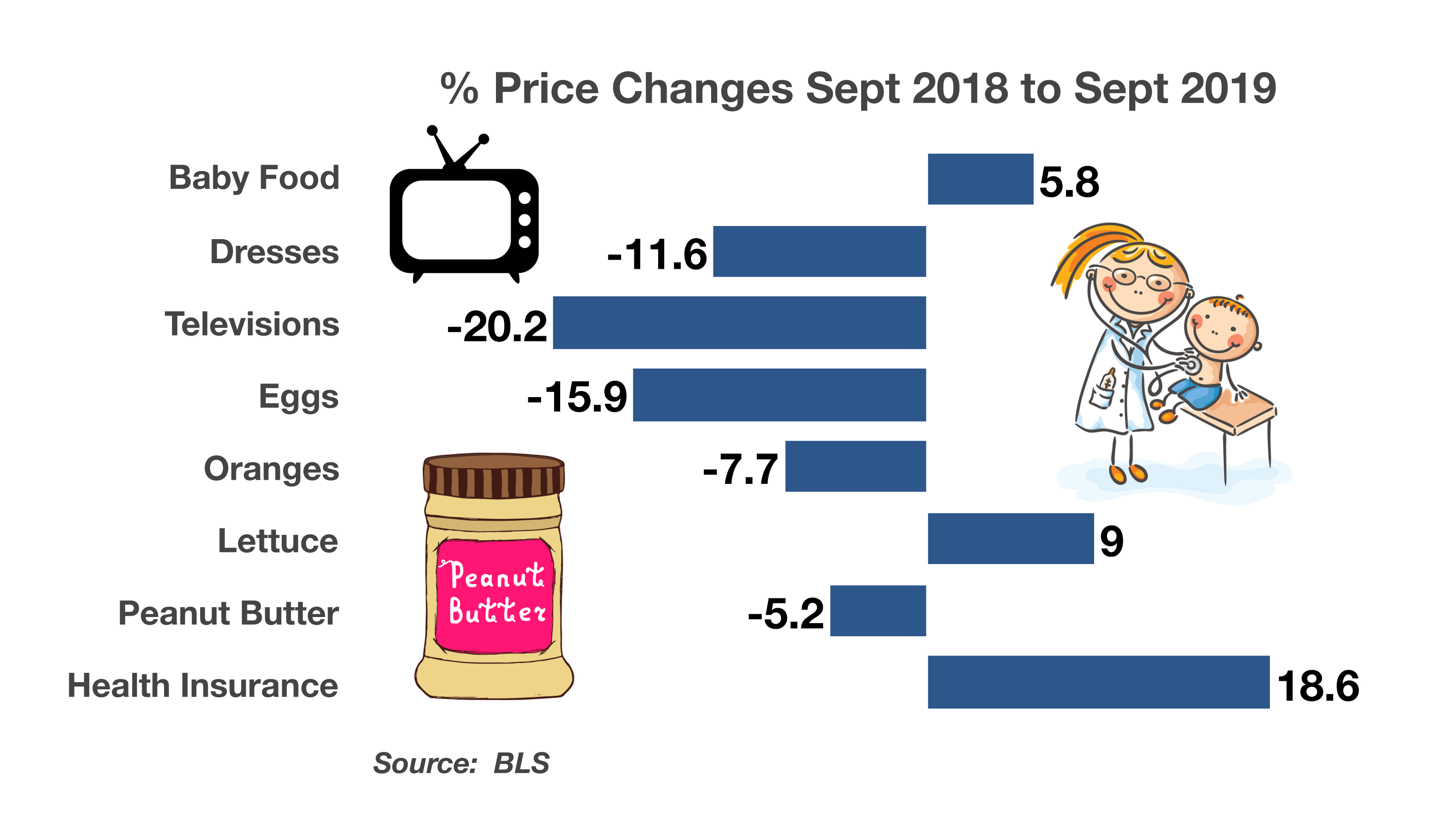
 Social Security Payments Increasing By 1.6% For 2020 – Retirement Planning
Social Security Payments Increasing By 1.6% For 2020 – Retirement Planning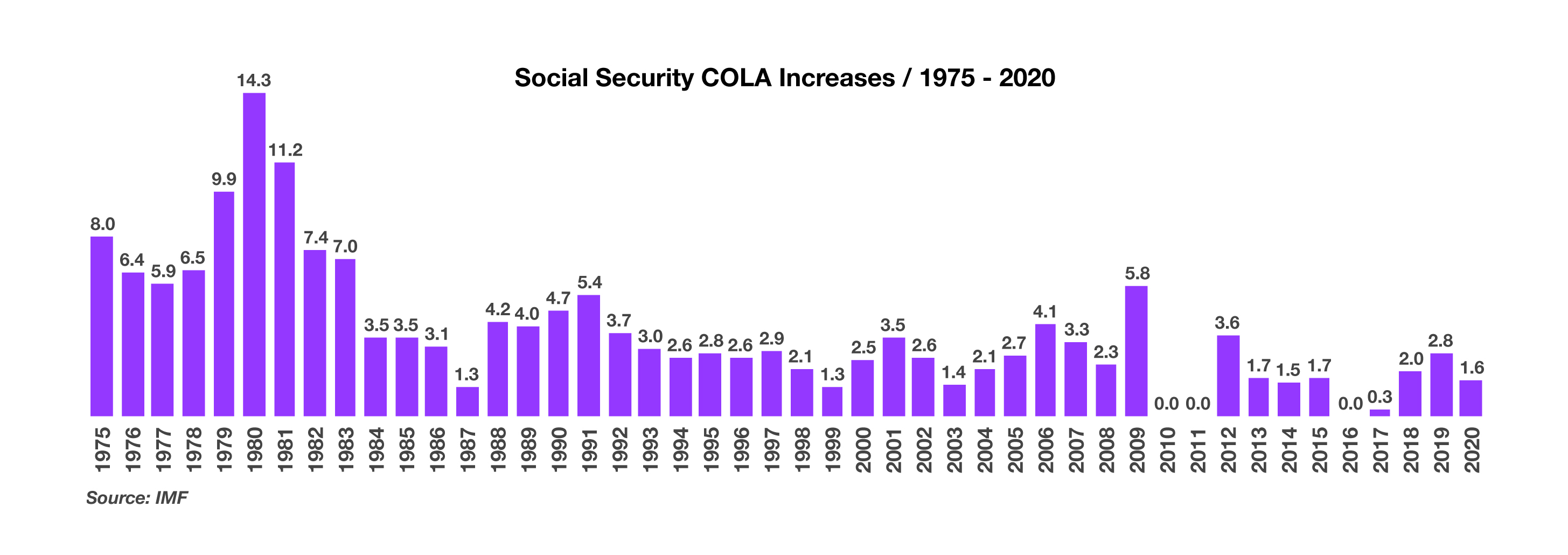
 Japanese Exports Fall
Japanese Exports Fall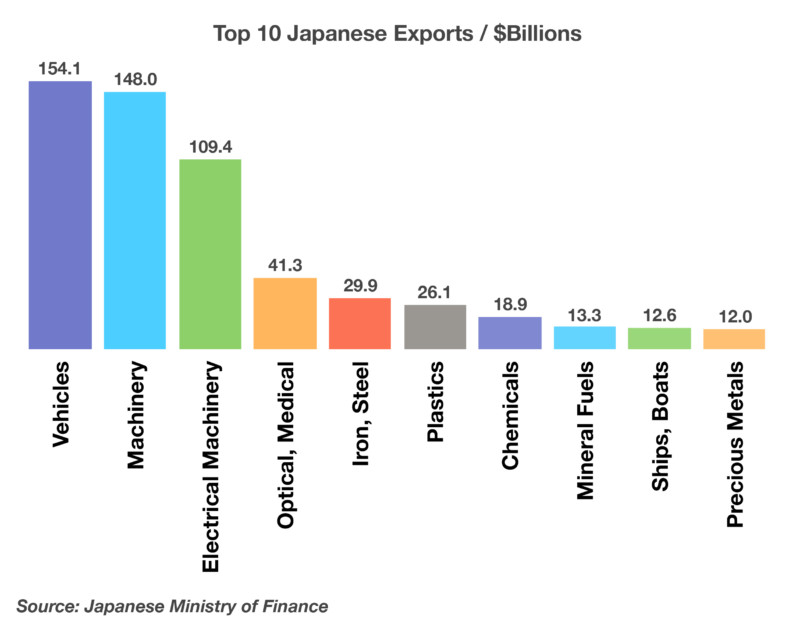 Data from the Japanese Ministry of Finance revealed a fall of 6.7% in exports to China over the past year and a drop of 7.9% to the U.S. over the same period.
Data from the Japanese Ministry of Finance revealed a fall of 6.7% in exports to China over the past year and a drop of 7.9% to the U.S. over the same period.