Jason Napoli, ChFC, AAMS, MBA
President and Chief Investment Officer
High Country Capital Management
970.249.3499
www.hccm.com
Stock Indices:
| Dow Jones | 42,270 |
| S&P 500 | 5,911 |
| Nasdaq | 19,113 |
Bond Sector Yields:
| 2 Yr Treasury | 3.89% |
| 10 Yr Treasury | 4.41% |
| 10 Yr Municipal | 3.31% |
| High Yield | 7.26% |
YTD Market Returns:
| Dow Jones | -0.64% |
| S&P 500 | 0.51% |
| Nasdaq | -1.02% |
| MSCI-EAFE | 17.30% |
| MSCI-Europe | 21.20% |
| MSCI-Pacific | 10.50% |
| MSCI-Emg Mkt | 8.90% |
| US Agg Bond | 2.45% |
| US Corp Bond | 2.26% |
| US Gov’t Bond | 2.44% |
Commodity Prices:
| Gold | 3,313 |
| Silver | 33.07 |
| Oil (WTI) | 60.79 |
Currencies:
| Dollar / Euro | 1.13 |
| Dollar / Pound | 1.34 |
| Yen / Dollar | 144.85 |
| Canadian /Dollar | 0.72 |
Macro Overview
A 15% tariff was imposed on roughly 40% of consumer products imported from China effective September 1st, affecting over $100 billion worth of annual imports. An additional slew of products from China is scheduled to be assessed a 15% tariff on December 15th, applicable to nearly everything imported from China by year end.
The announcement of additional tariffs on Chinese imports into the U.S. caused prolonged uncertainty surrounding the extent of the ongoing trade tensions. Since tariffs are dictated by trade policy, some believe that a potential delay or reversal of a portion of the scheduled tariffs is possible.
China let their currency, the yuan, fall in response to the U.S. decision to apply additional tariffs, thus weakening the Chinese currency and making Chinese exports more competitive internationally. Concurrently, the U.S. Treasury Department designated China as a currency manipulator in early August, a designation that addresses potential unfair trade practices. China’s currency fell 3.7% against the U.S. dollar in August, the single largest monthly drop in 25 years.
The Congressional Budget Office (CBO) estimates that the U.S. budget deficit will surpass $1 trillion in 2020 and continue to expand to over $1.3 trillion by 2029. The ten year projection is based on increasing tax revenue but with slower GDP growth of 1.8% per year.
Stocks have been resilient since the beginning of the year despite ongoing tariff threats, slowing global economy, softening earnings projections, and uncertainty surrounding international debt issues. All eleven sectors of the S&P 500 Index were still positive year to date as of the end of August.
Recession fears fueled volatility and uncertainty as bond yields continued to fall in August. Economists view higher short-term rates than long-term rates, also known as an inverted yield curve, as a signal of slowing economic growth in the future. Any validation of an upcoming recession is subjective with expectations varying from economist to economist.
Global yields continued their decline in August with 30-year German government bond yields falling below 0% while the 30-year U.S. Treasury bond yield dipped below 2% for the first time on record. Roughly $16 trillion worth of global bonds now carry negative yields, of historical significance in the fixed income markets.
Argentina is close to defaulting on its government debt, owing approximately $50 billion of long-term debt primarily held by foreign investors throughout the world. Argentina’s currency, the peso, fell 25% against the U.S. dollar in August, the steepest drop since its last currency crisis. (Sources: Commerce Dept., U.S. Treasury, Federal Reserve, CBO, Bloomberg, S&P)
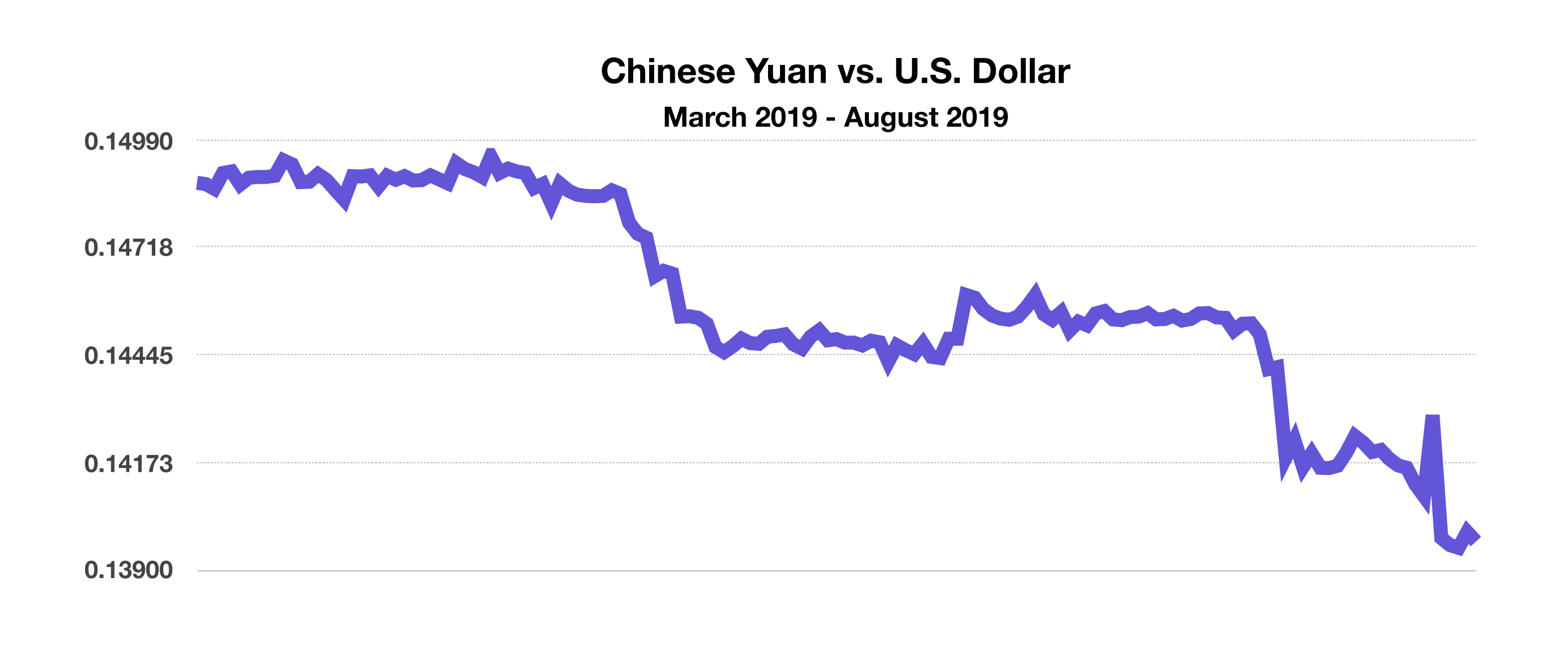
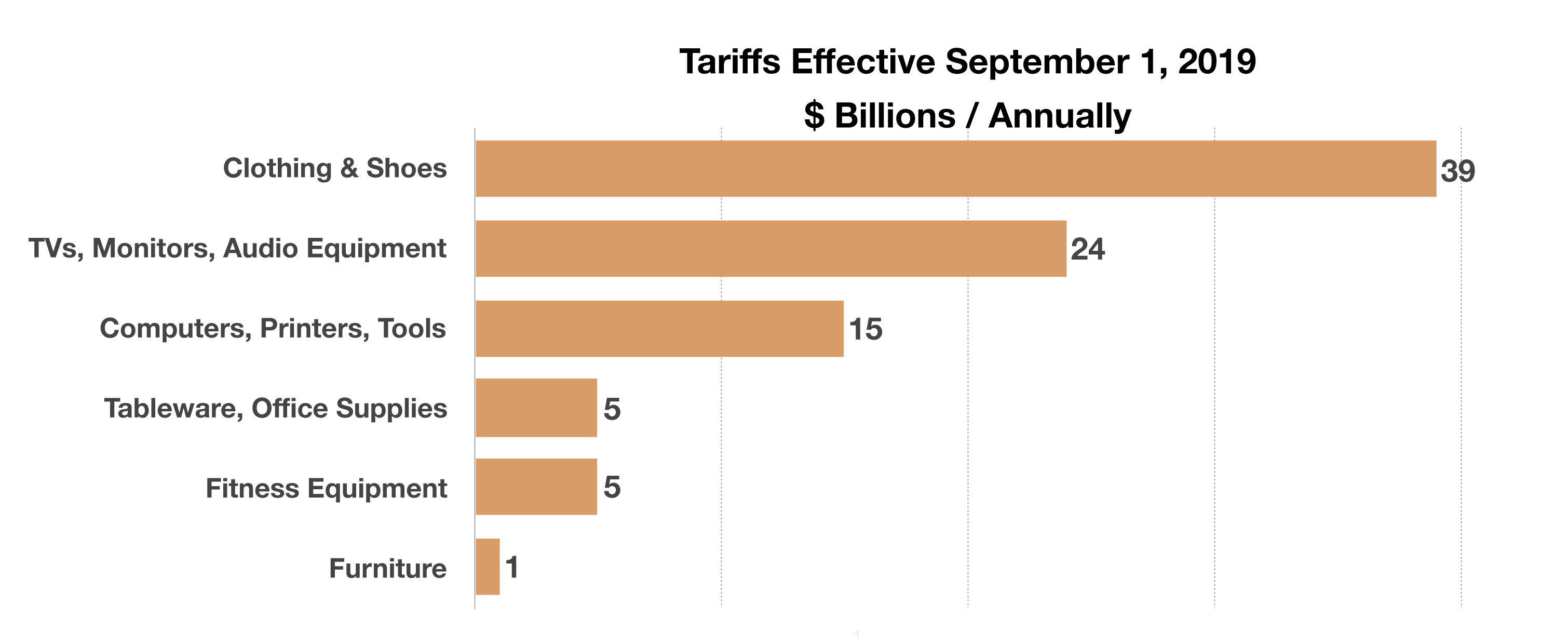
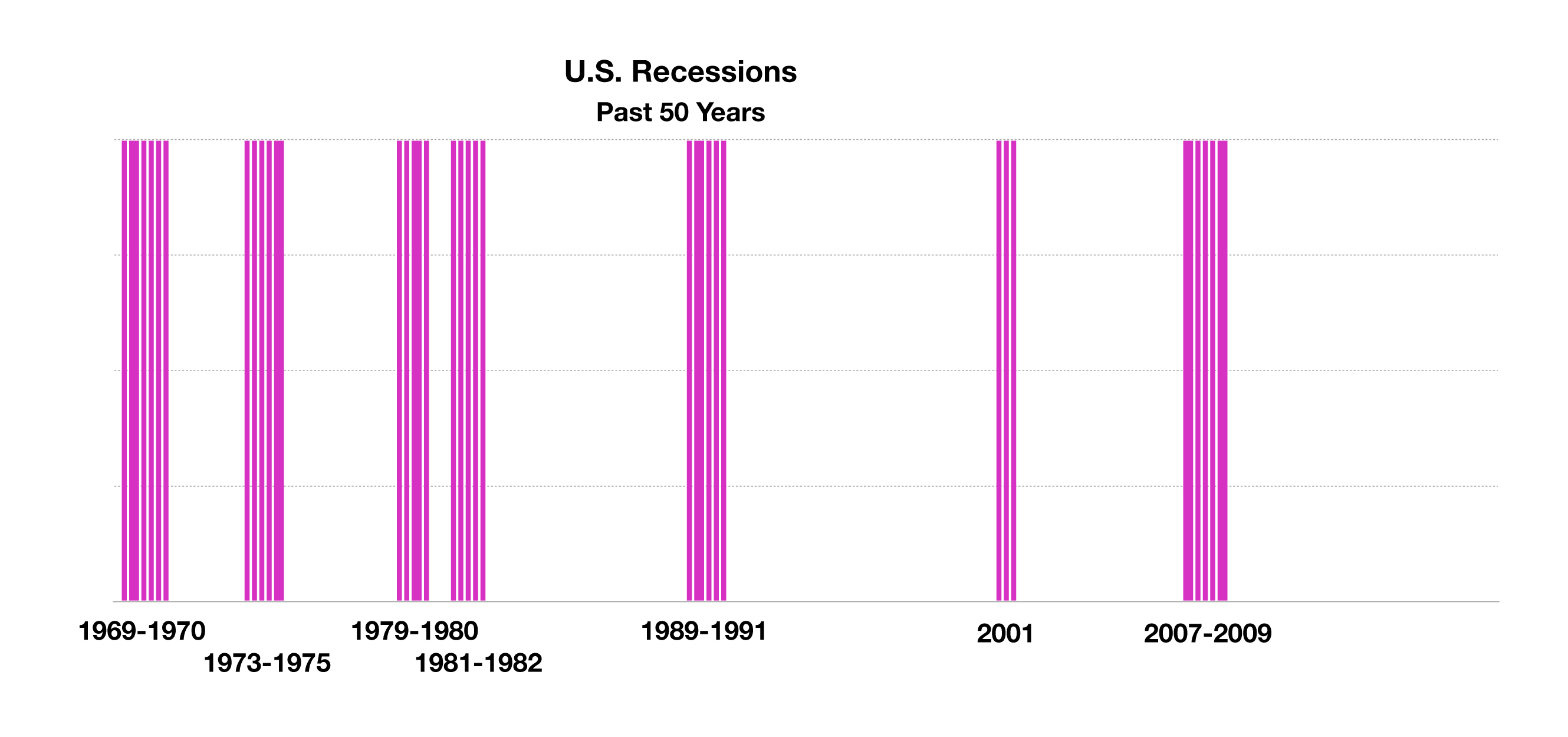
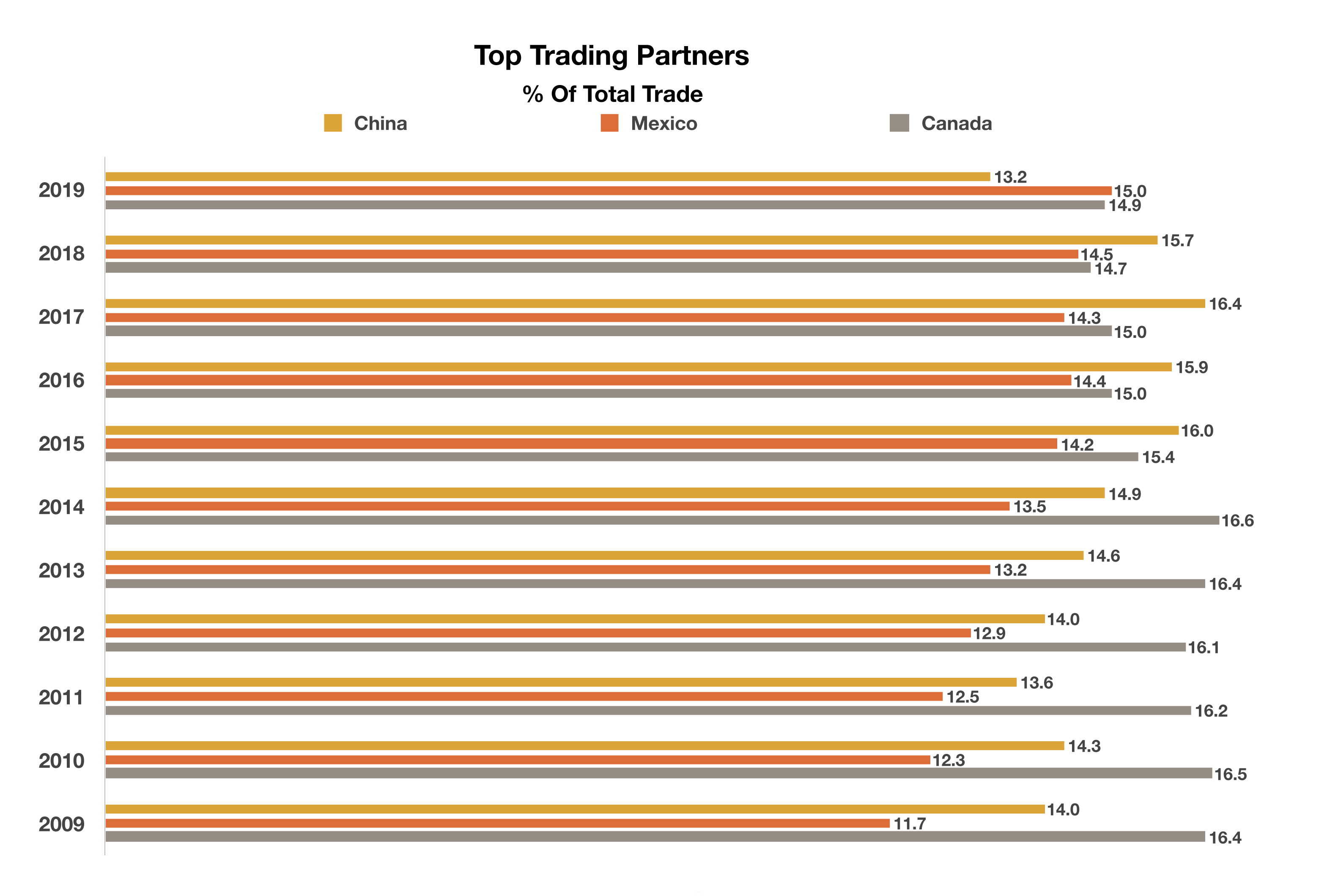
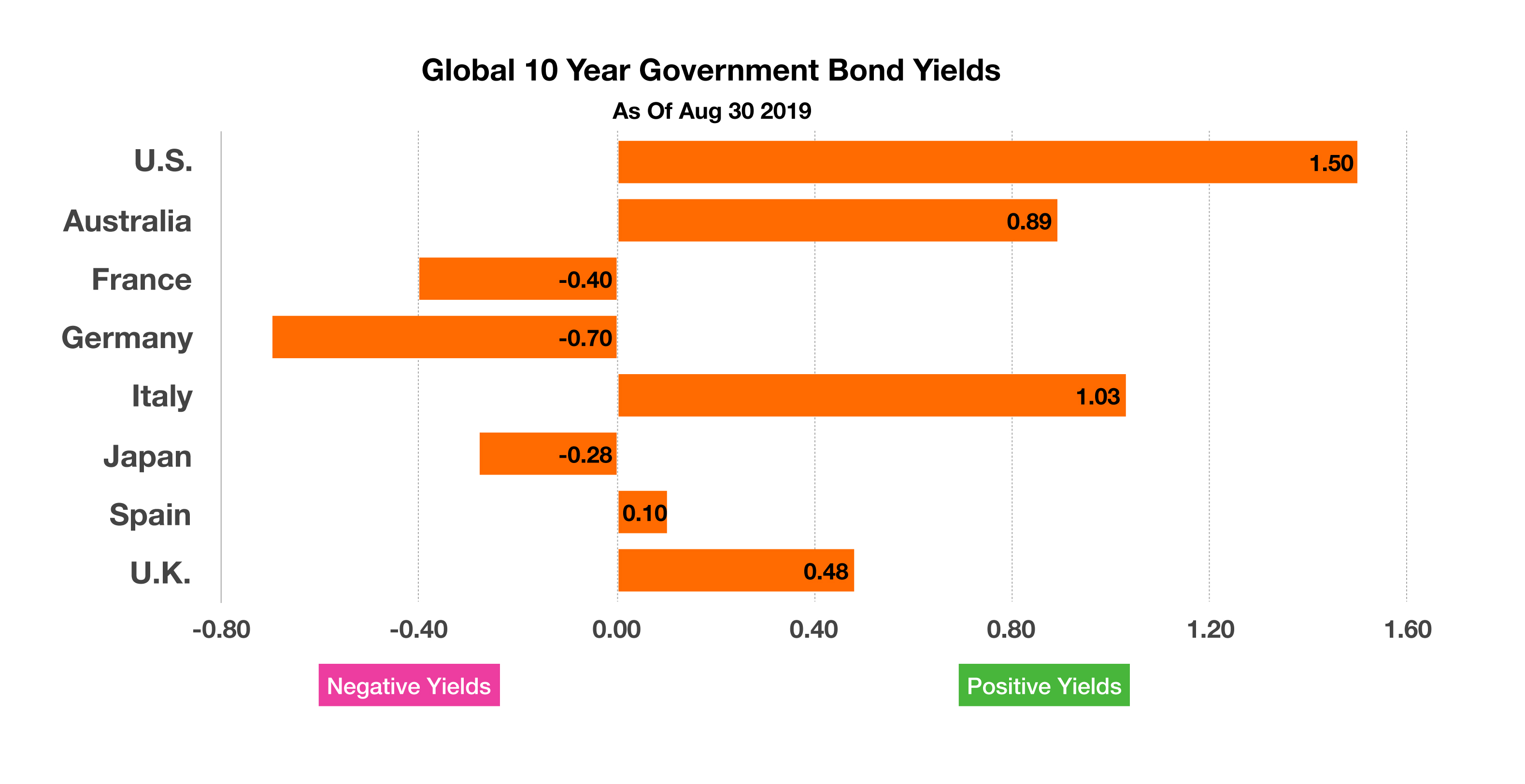 Developed countries whose 10-year government bond yields were below 0% as of the end of August include France, Germany and Japan. (Sources: Bloomberg, U.S. Treasury)
Developed countries whose 10-year government bond yields were below 0% as of the end of August include France, Germany and Japan. (Sources: Bloomberg, U.S. Treasury)